Page 333 -
P. 333
ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM: A SPECIAL-PURPOSE SOLUTION PROCEDURE 313
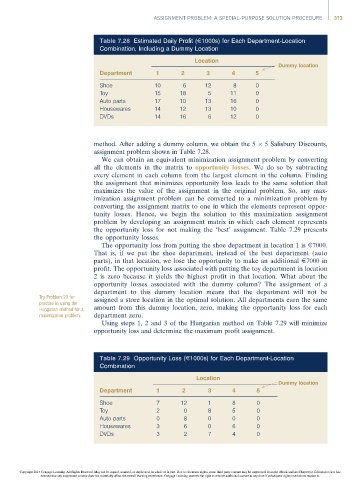
Table 7.28 Estimated Daily Profit (E1000s) for Each Department-Location
Combination, Including a Dummy Location
Location
Dummy location
Department 1 2 3 4 5
Shoe 10 6 12 8 0
Toy 15 18 5 11 0
Auto parts 17 10 13 16 0
Housewares 14 12 13 10 0
DVDs 14 16 6 12 0
method. After adding a dummy column, we obtain the 5 5 Salisbury Discounts,
assignment problem shown in Table 7.28.
We can obtain an equivalent minimization assignment problem by converting
all the elements in the matrix to opportunity losses.Wedosobysubtracting
every element in each column from the largest element in the column. Finding
the assignment that minimizes opportunity loss leads to the same solution that
maximizes the value of the assignment in the original problem. So, any max-
imization assignment problem can be converted to a minimization problem by
converting the assignment matrix to one in which the elements represent oppor-
tunity losses. Hence, we begin the solution to this maximization assignment
problem by developing an assignment matrix in which each element represents
the opportunity loss for not making the ‘best’ assignment. Table 7.29 presents
the opportunity losses.
The opportunity loss from putting the shoe department in location 1 is E7000.
That is, if we put the shoe department, instead of the best department (auto
parts), in that location, we lose the opportunity to make an additional E7000 in
profit. The opportunity loss associated with putting the toy department in location
2 is zero because it yields the highest profit in that location. What about the
opportunity losses associated with the dummy column? The assignment of a
department to this dummy location means that the department will not be
Try Problem 20 for assigned a store location in the optimal solution. All departments earn the same
practise in using the
Hungarian method for a amount from this dummy location, zero, making the opportunity loss for each
maximization problem. department zero.
Using steps 1, 2 and 3 of the Hungarian method on Table 7.29 will minimize
opportunity loss and determine the maximum profit assignment.
Table 7.29 Opportunity Loss (E1000s) for Each Department-Location
Combination
Location
Dummy location
Department 1 2 3 4 5
Shoe 7 12 1 8 0
Toy 2 0 8 5 0
Auto parts 0 8 0 0 0
Housewares 3 6 0 6 0
DVDs 3 2 7 4 0
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.