Page 198 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 198
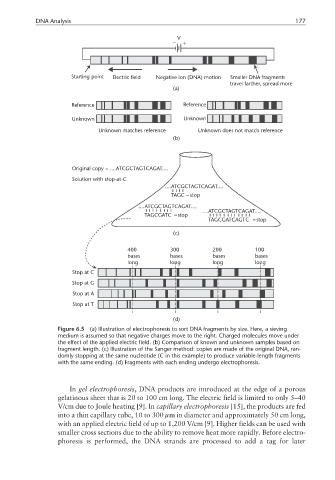
DNA Analysis 177
V
Starting point Electric field Negative ion (DNA) motion Smaller DNA fragments
travel farther, spread more
(a)
Reference Reference
Unknown Unknown
Unknown matches reference Unknown does not match reference
(b)
Original copy = ....ATCGCTAGTCAGAT....
Solution with stop-at-C
....ATCGCTAGTCAGAT....
TAGC stop
....ATCGCTAGTCAGAT....
....ATCGCTAGTCAGAT....
TAGCGATC stop
TAGCGATCAGTC stop
(c)
400 300 200 100
bases bases bases bases
long long long long
Stop at C
Stop at G
Stop at A
Stop at T
(d)
Figure 6.5 (a) Illustration of electrophoresis to sort DNA fragments by size. Here, a sieving
medium is assumed so that negative charges move to the right. Charged molecules move under
the effect of the applied electric field. (b) Comparison of known and unknown samples based on
fragment length. (c) Illustration of the Sanger method: copies are made of the original DNA, ran-
domly stopping at the same nucleotide (C in this example) to produce variable-length fragments
with the same ending. (d) Fragments with each ending undergo electrophoresis.
In gel electrophoresis, DNA products are introduced at the edge of a porous
gelatinous sheet that is 20 to 100 cm long. The electric field is limited to only 5–40
V/cm due to Joule heating [9]. In capillary electrophoresis [15], the products are fed
into a thin capillary tube, 10 to 300 µm in diameter and approximately 50 cm long,
with an applied electric field of up to 1,200 V/cm [9]. Higher fields can be used with
smaller cross sections due to the ability to remove heat more rapidly. Before electro-
phoresis is performed, the DNA strands are processed to add a tag for later