Page 127 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 127
Heat and mass transfers in the context of energy geostructures 99
Table 3.10 Specific heat and bulk density of selected materials.
3
Material Specific heat, c p [J/(kg C)] Bulk density, ρ [kg/m ]
Quartz 799 2650
Kaolin 937 2600
Calcium carbonate 870 2710
816 2450
CaSO 4
690 5240
Fe 2 O 3
908 3700
Al 2 O 3
946 3600
Fe(OH) 3
Orthoclase 812 2560
Oligaclase 858 2640
Potash mica 870 2900
Magnesia mica 862 2900
Hornblende 816 3200
Apatite 766 3200
Dolomite 929 2900
Talc 874 2700
Granite 803 2600
Syenite 833 2700
Diorite 812 2900
Andesite 833 2400
Basalt 891 3000
Source: Modified after Rees, S., Adjali, M., Zhou, Z., Davies, M. & Thomas, H., 2000. Ground heat
transfer effects on the thermal performance of earth-contact structures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev.
4 (3), 213 265. and Clark, S.P., 1966. Handbook of Physical Constants. Geological Society of America.
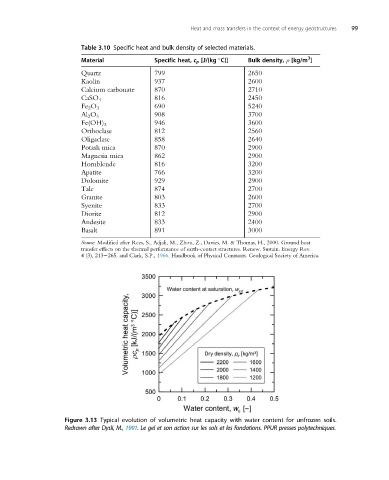
Figure 3.13 Typical evolution of volumetric heat capacity with water content for unfrozen soils.
Redrawn after Dysli, M., 1991. Le gel et son action sur les sols et les fondations. PPUR presses polytechniques.