Page 227 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 227
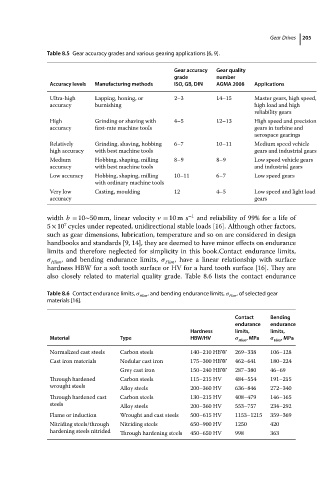
Table 8.5 Gear accuracy grades and various gearing applications [6, 9]. Gear Drives 205
Gear accuracy Gear quality
grade number
Accuracy levels Manufacturing methods ISO, GB, DIN AGMA 2008 Applications
Ultra-high Lapping, honing, or 2–3 14–15 Master gears, high speed,
accuracy burnishing high load and high
reliability gears
High Grinding or shaving with 4–5 12–13 High speed and precision
accuracy first-rate machine tools gears in turbine and
aerospace gearings
Relatively Grinding, shaving, hobbing 6–7 10–11 Medium speed vehicle
high accuracy with best machine tools gears and industrial gears
Medium Hobbing, shaping, milling 8–9 8–9 Low speed vehicle gears
accuracy with best machine tools and industrial gears
Low accuracy Hobbing, shaping, milling 10–11 6–7 Low speed gears
with ordinary machine tools
Very low Casting, moulding 12 4–5 Low speed and light load
accuracy gears
width b = 10∼50 mm, linear velocity v = 10 m s −1 and reliability of 99% for a life of
7
5 × 10 cycles under repeated, unidirectional stable loads [16]. Although other factors,
such as gear dimensions, lubrication, temperature and so on are considered in design
handbooks and standards [9, 14], they are deemed to have minor effects on endurance
limits and therefore neglected for simplicity in this book.Contact endurance limits,
Hlim , and bending endurance limits, Flim , have a linear relationship with surface
hardness HBW for a soft tooth surface or HV for a hard tooth surface [16]. They are
also closely related to material quality grade. Table 8.6 lists the contact endurance
Table 8.6 Contact endurance limits, Hlim , and bending endurance limits, Flim , of selected gear
materials [16].
Contact Bending
endurance endurance
Hardness limits, limits,
Material Type HBW/HV Hlim ,MPa Flim ,MPa
Normalized cast steels Carbon steels 140–210 HBW 269–338 106–128
Cast iron materials Nodular cast iron 175–300 HBW 462–641 180–224
Grey cast iron 150–240 HBW 287–380 46–69
Through hardened Carbon steels 115–215 HV 484–554 191–215
wrought steels Alloy steels 200–360 HV 636–846 272–340
Through hardened cast Carbon steels 130–215 HV 408–479 146–165
steels Alloy steels 200–360 HV 553–757 234–292
Flame or induction Wrought and cast steels 500–615 HV 1153–1215 359–369
Nitriding steels/through Nitriding steels 650–900 HV 1250 420
hardening steels nitrided Through hardening steels 450–650 HV 998 363