Page 261 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 261
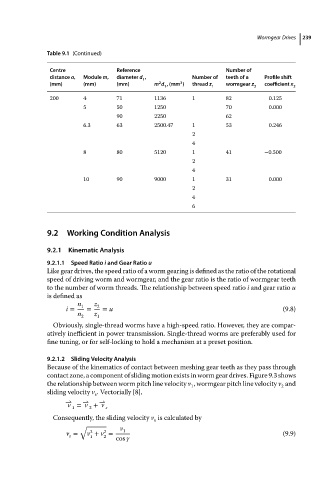
Table 9.1 (Continued) Wormgear Drives 239
Centre Reference Number of
distance a, Module m, diameter d , Number of teeth of a Profile shift
1
2
3
(mm) (mm) (mm) m d ,(mm ) thread z wormgear z coefficient x
1 1 2 2
200 4 71 1136 1 82 0.125
5 50 1250 70 0.000
90 2250 62
6.3 63 2500.47 1 53 0.246
2
4
8 80 5120 1 41 −0.500
2
4
10 90 9000 1 31 0.000
2
4
6
9.2 Working Condition Analysis
9.2.1 Kinematic Analysis
9.2.1.1 Speed Ratio i and Gear Ratio u
Like gear drives, the speed ratio of a worm gearing is defined as the ratio of the rotational
speed of driving worm and wormgear, and the gear ratio is the ratio of wormgear teeth
to the number of worm threads. The relationship between speed ratio i and gear ratio u
is defined as
n 1 z 2
i = = = u (9.8)
n 2 z 1
Obviously, single-thread worms have a high-speed ratio. However, they are compar-
atively inefficient in power transmission. Single-thread worms are preferably used for
fine tuning, or for self-locking to hold a mechanism at a preset position.
9.2.1.2 Sliding Velocity Analysis
Because of the kinematics of contact between meshing gear teeth as they pass through
contact zone, a component of sliding motion exists in worm gear drives. Figure 9.3 shows
the relationship between worm pitch line velocity v , wormgear pitch line velocity v and
1 2
sliding velocity v . Vectorially [8],
s
− ⇀ − ⇀ − ⇀
v = v + v s
1
2
Consequently, the sliding velocity v is calculated by
s
√ v
2
2
v = v + v = 1 (9.9)
s
2
1
cos