Page 262 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 262
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
240
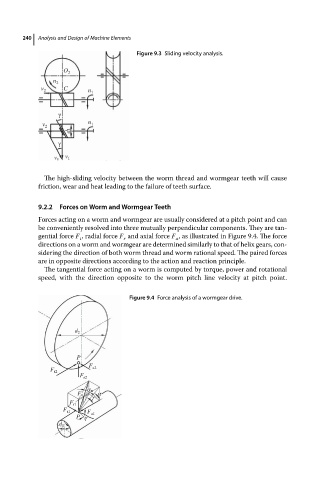
Figure 9.3 Sliding velocity analysis.
O 2
n 2
C
v 2
n 1
γ
n 1
v 2
d1
γ
v s v 1
The high-sliding velocity between the worm thread and wormgear teeth will cause
friction, wear and heat leading to the failure of teeth surface.
9.2.2 Forces on Worm and Wormgear Teeth
Forces acting on a worm and wormgear are usually considered at a pitch point and can
be conveniently resolved into three mutually perpendicular components. They are tan-
gential force F , radial force F and axial force F ,asillustratedinFigure9.4.Theforce
t
r
a
directions on a worm and wormgear are determined similarly to that of helix gears, con-
sidering the direction of both worm thread and worm rational speed. The paired forces
are in opposite directions according to the action and reaction principle.
The tangential force acting on a worm is computed by torque, power and rotational
speed, with the direction opposite to the worm pitch line velocity at pitch point.
Figure 9.4 Force analysis of a wormgear drive.
d 2
P
F t2 F a2
F r2
α n α
F n
γ
F r1
F t1 F a1
P γ
d 1