Page 420 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 420
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
398
14.3.1.2 Force Analysis
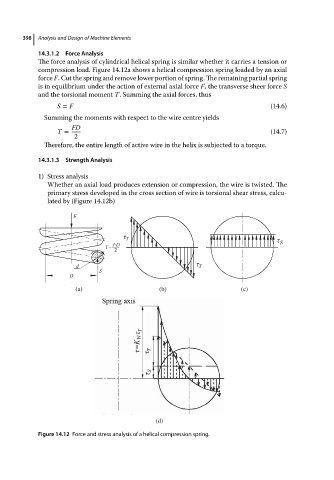
The force analysis of cylindrical helical spring is similar whether it carries a tension or
compression load. Figure 14.12a shows a helical compression spring loaded by an axial
force F. Cut the spring and remove lower portion of spring. The remaining partial spring
is in equilibrium under the action of external axial force F, the transverse sheer force S
and the torsional moment T. Summing the axial forces, thus
S = F (14.6)
Summing the moments with respect to the wire centre yields
FD
T = (14.7)
2
Therefore, the entire length of active wire in the helix is subjected to a torque.
14.3.1.3 Strength Analysis
1) Stress analysis
Whether an axial load produces extension or compression, the wire is twisted. The
primary stress developed in the cross section of wire is torsional shear stress, calcu-
lated by (Figure 14.12b)
(a) (b) (c)
(d)
Figure 14.12 Force and stress analysis of a helical compression spring.