Page 415 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 415
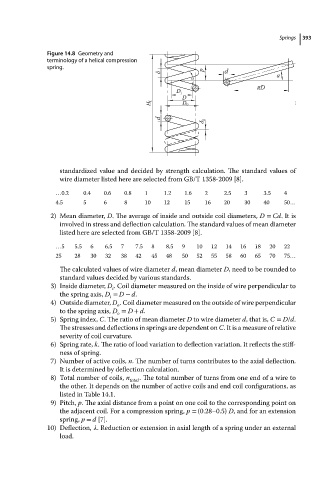
Figure 14.8 Geometry and Springs 393
terminology of a helical compression
spring.
standardized value and decided by strength calculation. The standard values of
wire diameter listed here are selected from GB/T 1358-2009 [8].
…0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.6 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
4.5 5 6 8 10 12 15 16 20 30 40 50…
2) Mean diameter, D. The average of inside and outside coil diameters, D = Cd.Itis
involved in stress and deflection calculation. The standard values of mean diameter
listed here are selected from GB/T 1358-2009 [8].
…5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5 8 8.5 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
25 28 30 32 38 42 45 48 50 52 55 58 60 65 70 75…
The calculated values of wire diameter d,meandiameter D, need to be rounded to
standard values decided by various standards.
3) Inside diameter, D . Coil diameter measured on the inside of wire perpendicular to
i
the spring axis, D = D − d.
i
4) Outside diameter, D . Coil diameter measured on the outside of wire perpendicular
o
to the spring axis, D = D + d.
o
5) Spring index, C. The ratio of mean diameter D to wire diameter d,thatis, C = D/d.
The stresses and deflections in springs are dependent on C.Itisameasureofrelative
severity of coil curvature.
6) Spring rate, k. The ratio of load variation to deflection variation. It reflects the stiff-
ness of spring.
7) Number of active coils, n. The number of turns contributes to the axial deflection.
It is determined by deflection calculation.
8) Total number of coils, n total . The total number of turns from one end of a wire to
the other. It depends on the number of active coils and end coil configurations, as
listed in Table 14.1.
9) Pitch, p. The axial distance from a point on one coil to the corresponding point on
the adjacent coil. For a compression spring, p = (0.28–0.5) D, and for an extension
spring, p = d [7].
10) Deflection, . Reduction or extension in axial length of a spring under an external
load.