Page 434 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 434
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
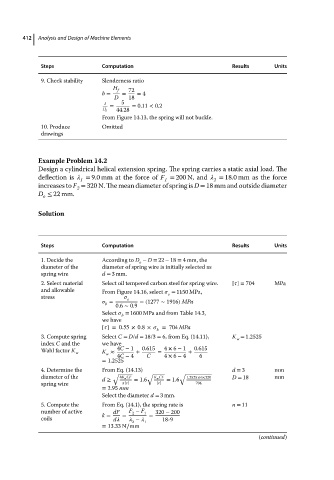
412
Steps Computation Results Units
9. Check stability Slenderness ratio
H 72
b = f = = 4
D 18
5
= = 0.11 < 0.2
H f 44.28
From Figure 14.13, the spring will not buckle.
10. Produce Omitted
drawings
Example Problem 14.2
Design a cylindrical helical extension spring. The spring carries a static axial load. The
deflection is = 9.0 mm at the force of F = 200 N, and = 18.0 mm as the force
1 1 2
increases to F = 320 N. The mean diameter of spring is D = 18 mm and outside diameter
2
D ≤ 22 mm.
o
Solution
Steps Computation Results Units
1. Decide the According to D − D = 22 − 18 = 4 mm, the
o
diameter of the diameter of spring wire is initially selected as
spring wire d = 3 mm.
2. Select material Select oil tempered carbon steel for spring wire. [ ] = 704 MPa
and allowable From Figure 14.16, select = 1150 MPa,
stress e e
= 0.6 ∼ 0.9 =(1277 ∼ 1916) MPa
b
Select = 1600 MPa and from Table 14.3,
b
we have
[ ]=0.55 × 0.8× = 704 MPa
b
3. Compute spring Select C = D/d = 18/3 = 6, from Eq. (14.11), K = 1.2525
w
index C and the we have
Wahl factor K w K ≈ 4C − 1 + 0.615 = 4 × 6 − 1 + 0.615
w
4C − 4
= 1.2525 C 4 × 6 − 4 6
4. Determine the From Eq. (14.13) d = 3 mm
√ √ √
diameter of the 8K w CF K w CF 1.2525×6×320 D = 18 mm
d ≥ = 1.6 = 1.6
spring wire [ ] [ ] 704
= 2.95 mm
Select the diameter d = 3 mm.
5. Compute the From Eq. (14.1), the spring rate is n = 11
number of active k = dF = F − F 1 = 320 − 200
2
coils d − 18-9
2 1
= 13.33 N∕mm
(continued)