Page 245 - Analysis, Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes, Third Edition
P. 245
Manufacturing and associated costs are most often reported in terms of $/yr. Information on a PFD is most
often reported in terms of kg or kmol per hour or per second. In order to calculate the yearly cost of raw
materials or utilities, the fraction of time that the plant is operating in a year must be known. This fraction
is known as the stream factor (SF), where
(8.5)
Typical values of the stream factor are in the range of 0.96 to 0.90. Even the most reliable and well-
managed plants will typically shut down for two weeks a year for scheduled maintenance, giving an SF =
0.96. Less reliable processes may require more downtime and hence lower SF values. The stream factor
represents the fraction of time that the process unit is on-line and operating at design capacity. When
estimating the size of equipment, care must be taken to use the design flowrate for a typical stream day
and not a calendar day. Example 8.8 illustrates the use of the stream factor.
Example 8.8
a. Determine the yearly cost of toluene for the process given in Chapter 1.
b. What is the yearly consumption of toluene?
c. What is the yearly revenue from the sale of benzene?
Assume a stream factor of 0.95, and note that the flowrates given on the PFD are in kilograms per stream
hour.
From Table 1.5, flowrate of toluene = 10,000 kg/h (Stream 1)
From Table 1.5, flowrate of benzene = 8210 kg/h (Stream 15)
From Table 8.5, cost of toluene = $0.648/kg
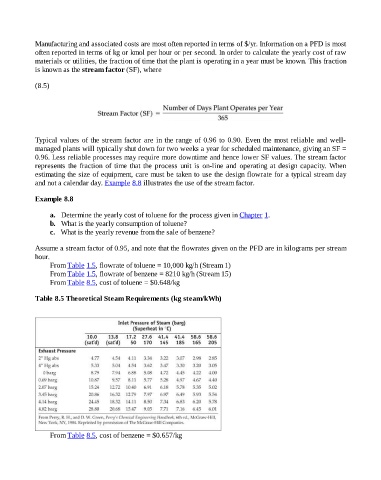
Table 8.5 Theoretical Steam Requirements (kg steam/kWh)
From Table 8.5, cost of benzene = $0.657/kg