Page 211 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 211
196 ELECTROCHEMICAL SENSORS
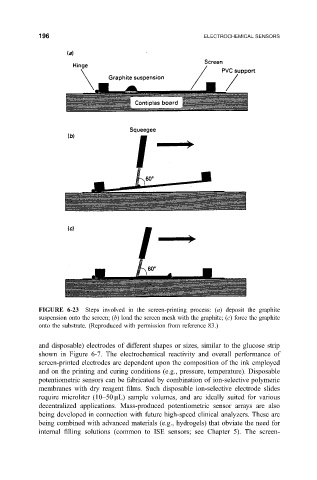
FIGURE 6-23 Steps involved in the screen-printing process: (a) deposit the graphite
suspension onto the screen; (b) load the screen mesh with the graphite; (c) force the graphite
onto the substrate. (Reproduced with permission from reference 83.)
and disposable) electrodes of different shapes or sizes, similar to the glucose strip
shown in Figure 6-7. The electrochemical reactivity and overall performance of
screen-printed electrodes are dependent upon the composition of the ink employed
and on the printing and curing conditions (e.g., pressure, temperature). Disposable
potentiometric sensors can be fabricated by combination of ion-selective polymeric
membranes with dry reagent ®lms. Such disposable ion-selective electrode slides
require microliter (10±50 mL) sample volumes, and are ideally suited for various
decentralized applications. Mass-produced potentiometric sensor arrays are also
being developed in connection with future high-speed clinical analyzers. These are
being combined with advanced materials (e.g., hydrogels) that obviate the need for
internal ®lling solutions (common to ISE sensors; see Chapter 5). The screen-