Page 66 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 66
2-3 SCANNING PROBE MICROSCOPY 51
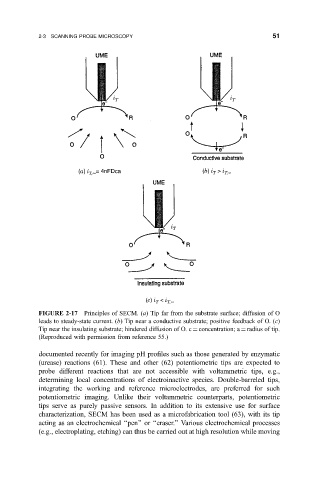
FIGURE 2-17 Principles of SECM. (a) Tip far from the substrate surface; diffusion of O
leads to steady-state current. (b) Tip near a conductive substrate; positive feedback of O. (c)
Tip near the insulating substrate; hindered diffusion of O. c concentration; a radius of tip.
(Reproduced with permission from reference 55.)
documented recently for imaging pH pro®les such as those generated by enzymatic
(urease) reactions (61). These and other (62) potentiometric tips are expected to
probe different reactions that are not accessible with voltammetric tips, e.g.,
determining local concentrations of electroinactive species. Double-barreled tips,
integrating the working and reference microelectrodes, are preferred for such
potentiometric imaging. Unlike their voltammetric counterparts, potentiometric
tips serve as purely passive sensors. In addition to its extensive use for surface
characterization, SECM has been used as a microfabrication tool (63), with its tip
acting as an electrochemical ``pen'' or ``eraser.'' Various electrochemical processes
(e.g., electroplating, etching) can thus be carried out at high resolution while moving