Page 192 - Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications
P. 192
Advanced Antennas for Radio Base Stations 165
20
18
16
Intracell handovers / (Erlang·hour) 14 8 6 Sector 120% gain
12
10
2 4 Array
0
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
Total number of deployed frequencies in the network
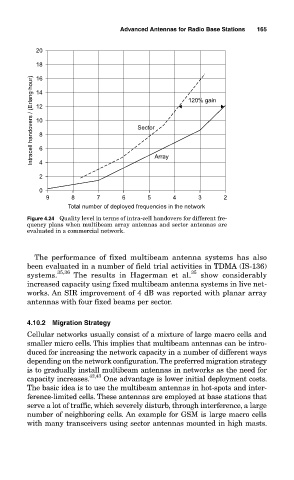
Figure 4.24 Quality level in terms of intra-cell handovers for different fre-
quency plans when multibeam array antennas and sector antennas are
evaluated in a commercial network.
The performance of fixed multibeam antenna systems has also
been evaluated in a number of field trial activities in TDMA (IS-136)
35
systems. 35,36 The results in Hagerman et al. show considerably
increased capacity using fixed multibeam antenna systems in live net-
works. An SIR improvement of 4 dB was reported with planar array
antennas with four fixed beams per sector.
4.10.2 Migration Strategy
Cellular networks usually consist of a mixture of large macro cells and
smaller micro cells. This implies that multibeam antennas can be intro-
duced for increasing the network capacity in a number of different ways
depending on the network configuration. The preferred migration strategy
is to gradually install multibeam antennas in networks as the need for
capacity increases. 42,43 One advantage is lower initial deployment costs.
The basic idea is to use the multibeam antennas in hot-spots and inter-
ference-limited cells. These antennas are employed at base stations that
serve a lot of traffic, which severely disturb, through interference, a large
number of neighboring cells. An example for GSM is large macro cells
with many transceivers using sector antennas mounted in high masts.