Page 74 - Anthropometry, Apparel Sizing and Design
P. 74
Developing apparel sizing system using anthropometric data 103
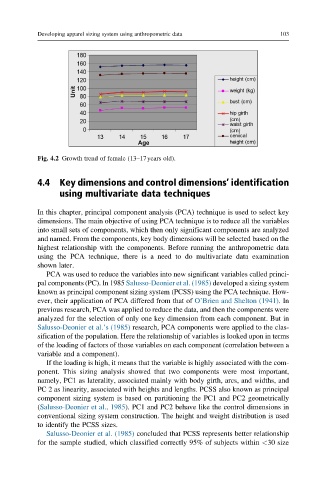
Fig. 4.2 Growth trend of female (13–17years old).
4.4 Key dimensions and control dimensions’ identification
using multivariate data techniques
In this chapter, principal component analysis (PCA) technique is used to select key
dimensions. The main objective of using PCA technique is to reduce all the variables
into small sets of components, which then only significant components are analyzed
and named. From the components, key body dimensions will be selected based on the
highest relationship with the components. Before running the anthropometric data
using the PCA technique, there is a need to do multivariate data examination
shown later.
PCA was used to reduce the variables into new significant variables called princi-
pal components (PC). In 1985 Salusso-Deonier et al. (1985) developed a sizing system
known as principal component sizing system (PCSS) using the PCA technique. How-
ever, their application of PCA differed from that of O’Brien and Shelton (1941).In
previous research, PCA was applied to reduce the data, and then the components were
analyzed for the selection of only one key dimension from each component. But in
Salusso-Deonier et al.’s (1985) research, PCA components were applied to the clas-
sification of the population. Here the relationship of variables is looked upon in terms
of the loading of factors of those variables on each component (correlation between a
variable and a component).
If the loading is high, it means that the variable is highly associated with the com-
ponent. This sizing analysis showed that two components were most important,
namely, PC1 as laterality, associated mainly with body girth, arcs, and widths, and
PC 2 as linearity, associated with heights and lengths. PCSS also known as principal
component sizing system is based on partitioning the PC1 and PC2 geometrically
(Salusso-Deonier et al., 1985). PC1 and PC2 behave like the control dimensions in
conventional sizing system construction. The height and weight distribution is used
to identify the PCSS sizes.
Salusso-Deonier et al. (1985) concluded that PCSS represents better relationship
for the sample studied, which classified correctly 95% of subjects within <30 size