Page 349 - Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB
P. 349
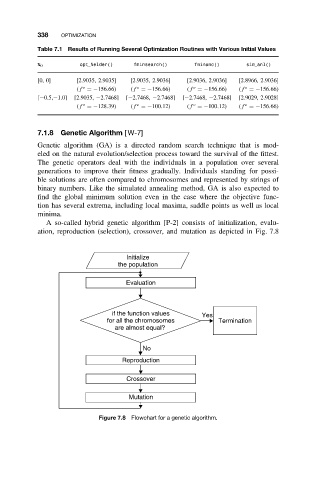
338 OPTIMIZATION
Table 7.1 Results of Running Several Optimization Routines with Various Initial Values
x 0 opt Nelder() fminsearch() fminunc() sim anl()
[0, 0] [2.9035, 2.9035] [2.9035, 2.9036] [2.9036, 2.9036] [2.8966, 2.9036]
o
o
o
o
(f =−156.66) (f =−156.66) (f =−156.66) (f =−156.66)
[−0.5,−1.0] [2.9035, −2.7468] [−2.7468, −2.7468] [−2.7468, −2.7468] [2.9029, 2.9028]
o
o
o
o
(f =−128.39) (f =−100.12) (f =−100.12) (f =−156.66)
7.1.8 Genetic Algorithm [W-7]
Genetic algorithm (GA) is a directed random search technique that is mod-
eled on the natural evolution/selection process toward the survival of the fittest.
The genetic operators deal with the individuals in a population over several
generations to improve their fitness gradually. Individuals standing for possi-
ble solutions are often compared to chromosomes and represented by strings of
binary numbers. Like the simulated annealing method, GA is also expected to
find the global minimum solution even in the case where the objective func-
tion has several extrema, including local maxima, saddle points as well as local
minima.
A so-called hybrid genetic algorithm [P-2] consists of initialization, evalu-
ation, reproduction (selection), crossover, and mutation as depicted in Fig. 7.8
Initialize
the population
Evaluation
if the function values Yes
for all the chromosomes Termination
are almost equal?
No
Reproduction
Crossover
Mutation
Figure 7.8 Flowchart for a genetic algorithm.