Page 443 - Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB
P. 443
432 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
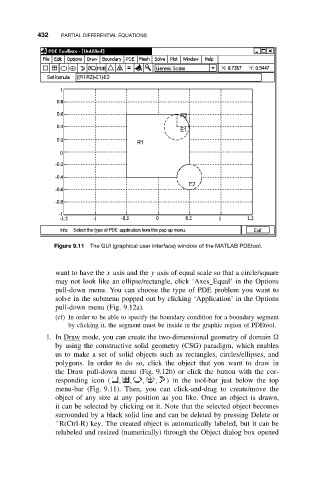
Figure 9.11 The GUI (graphical user interface) window of the MATLAB PDEtool.
want to have the x axis and the y axis of equal scale so that a circle/square
may not look like an ellipse/rectangle, click ‘Axes Equal’ in the Options
pull-down menu. You can choose the type of PDE problem you want to
solve in the submenu popped out by clicking ‘Application’ in the Options
pull-down menu (Fig. 9.12a).
(cf) In order to be able to specify the boundary condition for a boundary segment
by clicking it, the segment must be inside in the graphic region of PDEtool.
1. In Draw mode, you can create the two-dimensional geometry of domain
by using the constructive solid geometry (CSG) paradigm, which enables
us to make a set of solid objects such as rectangles, circles/ellipses, and
polygons. In order to do so, click the object that you want to draw in
the Draw pull-down menu (Fig. 9.12b) or click the button with the cor-
responding icon ( , , , , ) in the tool-bar just below the top
menu-bar (Fig. 9.11). Then, you can click-and-drag to create/move the
object of any size at any position as you like. Once an object is drawn,
it can be selected by clicking on it. Note that the selected object becomes
surrounded by a black solid line and can be deleted by pressing Delete or
R(Ctrl-R) key. The created object is automatically labeled, but it can be
∧
relabeled and resized (numerically) through the Object dialog box opened