Page 133 - Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
P. 133
Rock strengths and rock failure criteria 125
(3) Specific volume, v,isdefined as:
v ¼ 1 þ e (3.74)
where e is the void ratio and can be related to porosity by e ¼ f/(1 f).
The yield functions of the Cam-Clay and modified Cam-Clay models
are determined from the following equations:
Cam-Clay:
p 0
0
q þ Mp ln ¼ 0 (3.75)
p 0
0
Modified Cam-Clay:
q 2 þ M 2 p 0 0
p 02 1 p 0 ¼ 0 (3.76)
0
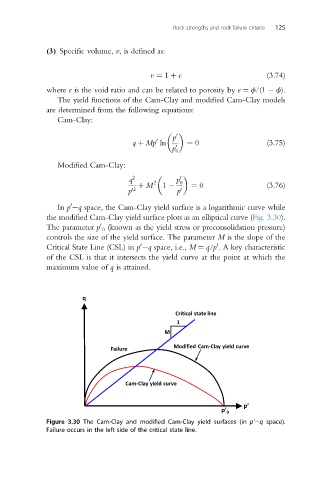
In p eq space, the Cam-Clay yield surface is a logarithmic curve while
the modified Cam-Clay yield surface plots as an elliptical curve (Fig. 3.30).
The parameter p 0 (known as the yield stress or preconsolidation pressure)
0
controls the size of the yield surface. The parameter M is the slope of the
Critical State Line (CSL) in p eq space, i.e., M ¼ q/p . A key characteristic
0
0
of the CSL is that it intersects the yield curve at the point at which the
maximum value of q is attained.
q
Critical state line
1
M
Modified Cam-Clay yield curve
Failure
Cam-Clay yield curve
p’
p’ 0
Figure 3.30 The Cam-Clay and modified Cam-Clay yield surfaces (in p’eq space).
Failure occurs in the left side of the critical state line.