Page 219 - Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
P. 219
214 Applied Petroleum Geomechanics
Cheng, 1988). This breakdown pressure can be used as the lower bound
breakdown pressure:
3s h s H 2hp p þ T 0
p bl ¼ (6.55)
2ð1 hÞ
The maximum horizontal stress for permeable rocks can be obtained
from the above equation:
(6.56)
s H ¼ 3s h 2ð1 hÞp b 2hp p þ T 0
where h ¼ a 1 2n .
2ð1 nÞ
Eqs. (6.56) and (6.53) can be used as the lower bound maximum
horizontal stress, while the upper bound maximum horizontal stress can be
obtained from Eq. (6.51).
6.4.2 Maximum horizontal stress from drilling-induced
tensile fractures
6.4.2.1 In normal and strike-slip faulting stress regimes
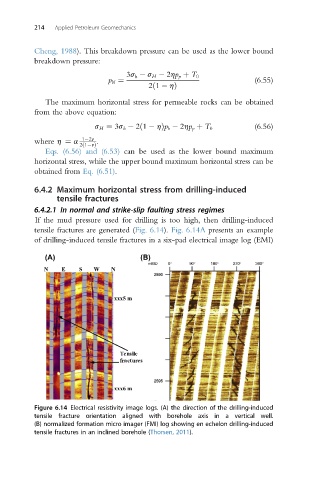
If the mud pressure used for drilling is too high, then drilling-induced
tensile fractures are generated (Fig. 6.14). Fig. 6.14A presents an example
of drilling-induced tensile fractures in a six-pad electrical image log (EMI)
(A) (B)
W
N N E E S S W NN
xxx5 mxxx5 m
Te
n
l
i
s
Tensilee
fr a c t u r es
fractureees
xxx6 mxxx6 m
Figure 6.14 Electrical resistivity image logs. (A) the direction of the drilling-induced
tensile fracture orientation aligned with borehole axis in a vertical well.
(B) normalized formation micro imager (FMI) log showing en echelon drilling-induced
tensile fractures in an inclined borehole (Thorsen, 2011).