Page 309 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 309
Step 3—Determine array size for each of the four designs
The ‘design insolation in the plane of the array’ (POA) can be determined from the
appropriate nomogram. By reading off the POA for different tilt angles (i.e. one
nomogram exists for each tilt angle), the tilt angle is easily optimised by selecting the
one that gives the maximum POA value. These values are, of course, a function of
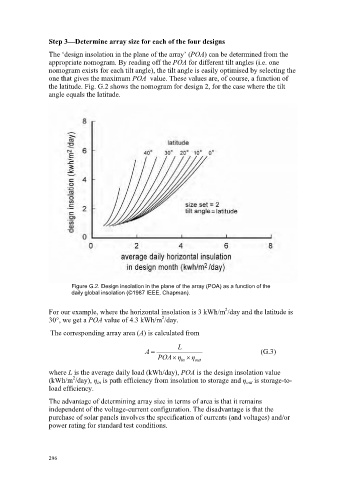
the latitude. Fig. G.2 shows the nomogram for design 2, for the case where the tilt
angle equals the latitude.
Figure G.2. Design insolation in the plane of the array (POA) as a function of the
daily global insolation (©1987 IEEE, Chapman).
2
For our example, where the horizontal insolation is 3 kWh/m /day and the latitude is
2
30°, we get a POA value of 4.3 kWh/m /day.
The corresponding array area (A) is calculated from
L
A (G.3)
POAu Ș u Ș
in out
where L is the average daily load (kWh/day), POA is the design insolation value
2
(kWh/m /day), Ș in is path efficiency from insolation to storage and Ș out is storage-to-
load efficiency.
The advantage of determining array size in terms of area is that it remains
independent of the voltage-current configuration. The disadvantage is that the
purchase of solar panels involves the specification of currents (and voltages) and/or
power rating for standard test conditions.
296