Page 45 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 45
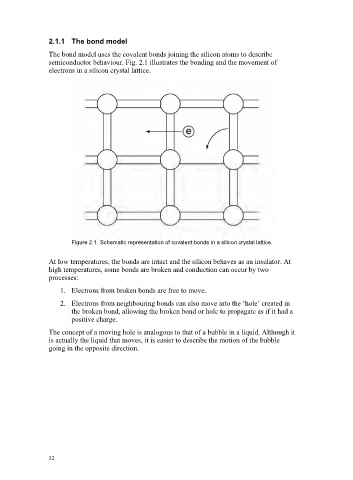
2.1.1 The bond model
The bond model uses the covalent bonds joining the silicon atoms to describe
semiconductor behaviour. Fig. 2.1 illustrates the bonding and the movement of
electrons in a silicon crystal lattice.
Figure 2.1. Schematic representation of covalent bonds in a silicon crystal lattice.
At low temperatures, the bonds are intact and the silicon behaves as an insulator. At
high temperatures, some bonds are broken and conduction can occur by two
processes:
1. Electrons from broken bonds are free to move.
2. Electrons from neighbouring bonds can also move into the ‘hole’ created in
the broken bond, allowing the broken bond or hole to propagate as if it had a
positive charge.
The concept of a moving hole is analogous to that of a bubble in a liquid. Although it
is actually the liquid that moves, it is easier to describe the motion of the bubble
going in the opposite direction.
32