Page 46 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 46
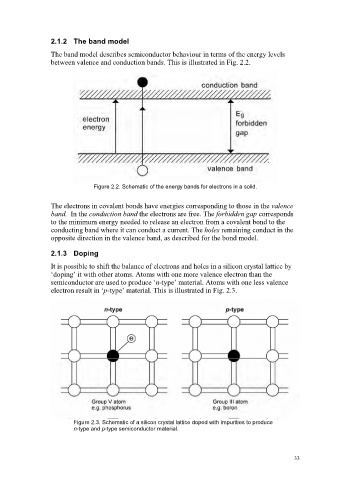
2.1.2 The band model
The band model describes semiconductor behaviour in terms of the energy levels
between valence and conduction bands. This is illustrated in Fig. 2.2.
Figure 2.2. Schematic of the energy bands for electrons in a solid.
The electrons in covalent bonds have energies corresponding to those in the valence
band. In the conduction band the electrons are free. The forbidden gap corresponds
to the minimum energy needed to release an electron from a covalent bond to the
conducting band where it can conduct a current. The holes remaining conduct in the
opposite direction in the valence band, as described for the bond model.
2.1.3 Doping
It is possible to shift the balance of electrons and holes in a silicon crystal lattice by
‘doping’ it with other atoms. Atoms with one more valence electron than the
semiconductor are used to produce ‘n-type’ material. Atoms with one less valence
electron result in ‘p-type’ material. This is illustrated in Fig. 2.3.
Figure 2.3. Schematic of a silicon crystal lattice doped with impurities to produce
n-type and p-type semiconductor material.
33