Page 47 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 47
2.2 SEMICONDUCTOR TYPES
Silicon and other semiconductor materials used for solar cells can be crystalline,
multicrystalline, polycrystalline, microcrystalline or amorphous. Although usages of
these terms vary, we follow the definitions by planar grain size according to Basore
(1994). Microcrystalline material has grains smaller than 1 ȝm, polycrystalline
smaller than 1 mm and multicrystalline smaller than 10 cm. The structure of the
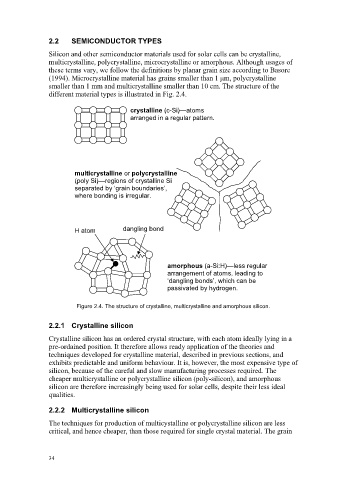
different material types is illustrated in Fig. 2.4.
crystalline (c-Si)—atoms
arranged in a regular pattern.
multicrystalline or polycrystalline
(poly Si)—regions of crystalline Si
separated by ‘grain boundaries’,
where bonding is irregular.
H atom dangling bond
amorphous (a-Si:H)—less regular
arrangement of atoms, leading to
‘dangling bonds’, which can be
passivated by hydrogen.
Figure 2.4. The structure of crystalline, multicrystalline and amorphous silicon.
2.2.1 Crystalline silicon
Crystalline silicon has an ordered crystal structure, with each atom ideally lying in a
pre-ordained position. It therefore allows ready application of the theories and
techniques developed for crystalline material, described in previous sections, and
exhibits predictable and uniform behaviour. It is, however, the most expensive type of
silicon, because of the careful and slow manufacturing processes required. The
cheaper multicrystalline or polycrystalline silicon (poly-silicon), and amorphous
silicon are therefore increasingly being used for solar cells, despite their less ideal
qualities.
2.2.2 Multicrystalline silicon
The techniques for production of multicystalline or polycrystalline silicon are less
critical, and hence cheaper, than those required for single crystal material. The grain
34