Page 132 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 132
118 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
(text continued from page 115) Flow of gases and vapors (compressible fluids) through
q = cu ft/sec at flowing conditions (Figure 2-37) Coef- nozzles and orifices. (For flow field importance see Refer-
ficient from Reference [22] for liquids discharge ences [31]). From [3]:
r, = critical pressure ratio for compressible flow, =
P',/P'l
q = YC'A , cu ft/sec
(at flowing conditions ) (2-48)
Y = net expansion factor from Figures 2-38A or 2-38B
AP = differential pressure (equal to inlet gauge pressure when
discharging to atmosphere)
p = weight density of fluid, lbs/cu ft at flowing conditions
A = cross section of orifice or nozzle, sq ft
C' = flow coefficient from Figures 2-38A or 2-38B
or, W = 1891 Yd,'C' E, lbs/hr (2-95)
where do = internal diameter of orifice, in
= specific volume of fluid, cu ft/lb
AP Pl
or, q'= ll.3OYd0'C'
at 14.7 psia and 600F (2-96)
where S, = Sp Gr gas relative to air, = mol wt. gas/29
T1 = absolute temperature, "R
P'1 = pressure, psi abs
k = CPj'C~
P' = psia Procedure
B = ratio small-to-large diameter in orifices and nozzles, A. How to determine pipe size for given capacity and pressure
and contractions or enlargements in pipes
drop.
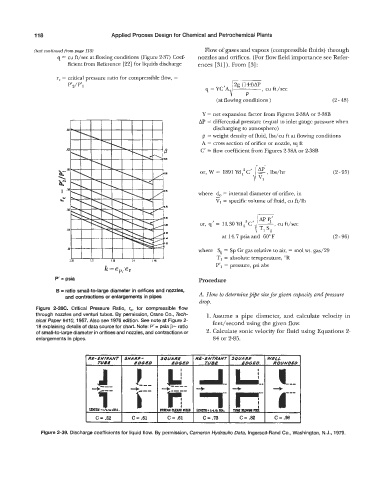
Figure 2-38C. Critical Pressure Ratio, r,, for compressible flow
through nozzles and venturi tubes. By permission, Crane Co., Tech- 1. Assume a pipe diameter, and calculate velocity in
nical Paper #NO, 1957. Also see 1976 edition. See note at Figure 2- feet/second using the given flow.
18 explaining details of data source for chart. Note: P' = psia p= ratio
+:zr , dDGED TUB€ BDGED ROUND€O
of small-to-large diameter in orifices and nozzles, and contractions or 2. Calculate sonic velocity for fluid using Equations 2-
4i-- +ip;- +I' +m- ,---
enlargements in pipes. 84 or 2-85.
M-INtffANr SUARP- 54UAR€ R€- €NTRANT SQUARE W€LL
TU8i
ED&?D
J ! --- U-l--I..C-- ----
*~lrt.iDtA. mu(cuulmnIs mtm*++bm. l~ummnna +
C = .52 C = .61 C = .61 c = .73 C = .82 C=.M