Page 291 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume II
P. 291
280 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
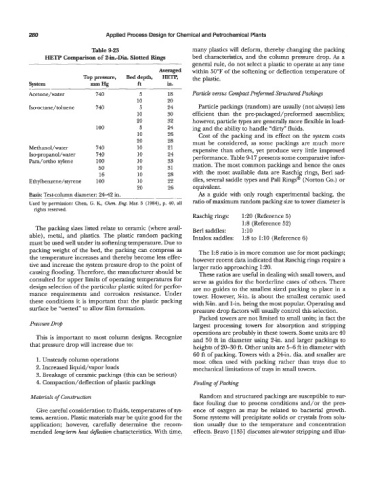
Table 9-23 many plastics will deform, thereby changing the packing
HEW Comparison of 2-h-Dia. Slotted Rings bed characteristics, and the column pressure drop. As a
general rule, do not select a plastic to operate at any time
Averaged within 50°F of the softening or deflection temperature of
Top p~ss~, Bed depth, mTP, the plastic.
System =Hg ft in.
Acetone/water 740 5 18 Particle versus Cmpact Prejimd Structured Packings
-
10 20
Iso-octane/ toluene 740 3 24 Particle packings (random) are usually (not always) less
10 30 efficient than the pre-packaged/preformed assemblies;
20 32 however, particle types are generally more flexible in load-
100 5 24 ing and the ability to handle “dirty” fluids.
10 26 Cost of the packing and its effect on the system costs
20 28 must be considered, as some packings are much more
Methanol/water 740 10 21 expensive than others, yet produce very little improved
Iso-propanol/water 740 10 24 performance. Table 9-1 7 presents some comparative infor-
Para/ortho xylene 100 10 33
50 10 31 mation. The most common packings and hence the ones
16 10 28 with the most available data are Raschig rings, Berl sad-
Ethylbenzene/styrene 100 10 22 dles, several saddle types and Pall Rings@ (Norton Co.) or
20 26 equivalent.
Basis: Test-column diameter: 24-42 in. As a guide with only rough experimental backing, the
Used by permission: Chen, G. IC, Chem. En6 Mar. 5 (1984), p. 40, all ratio of maximum random packing size to tower diameter is
rights reserved.
Raschig rings: 1:20 (Reference 5)
1:8 (Reference 52)
The packing sizes listed relate to ceramic (where avail- Berl saddles: 1:lO
able), metal, and plastics. The plastic random packing Intalox saddles: 1:8 to 1:lO (Reference 6)
must be used well under its softening temperature. Due to
packing weight of the bed, the packing can compress as The 1:8 ratio is in more common use for most packings;
the temperature increases and thereby become less effec- however recent data indicated that Raschig rings require a
tive and increase the system pressure drop to the point of larger ratio approaching 1:20.
causing flooding. Therefore, the manufacturer should be These ratios are useful in dealing with small towers, and
consulted for upper limits of operating temperatures for serve as guides for the borderline cases of others. There
design selection of the particular plastic suited for perfor- are no guides to the smallest sized packing to place in a
mance requirements and corrosion resistance. Under tower. However, %in. is about the smallest ceramic used
these conditions it is important that the plastic packing with %in. and 1-in. being the most popular. Operating and
surface be “wetted” to allow film formation. pressure drop factors will usually control this selection.
Packed towers are not limited to small units; in fact the
Pressure Drop largest processing towers for absorption and stripping
operations are probably in these towers. Some units are 40
This is important to most column designs. Recognize and 50 ft in diameter using 2-in. and larger packings to
that pressure drop will increase due to: heights of 20-30 ft. Other units are 5-6 ft in diameter with
60 ft of packing. Towers with a 24in. dia. and smaller are
1. Unsteady column operations most often used with packing rather than trays due to
2. Increased liquid/vapor loads mechanical limitations of trays in small towers.
3. Breakage of ceramic packings (this can be serious)
4. Compaction/deflection of plastic packings Fouling of Packing
Materials of Construction Random and structured packings are susceptible to sur-
face fouling due to process conditions and/or the pres
Give careful consideration to fluids, temperatures of sys- ence of oxygen as may be related to bacterial growth.
tems, aeration. Plastic materials may be quite good for the Some systems will precipitate solids or crystals from solu-
application; however, carefully determine the recom- tion usually due to the temperature and concentration
mended long-term heat &fiction characteristics. With time, effects. Bravo [ 1351 discusses air-water stripping and illus-