Page 37 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume II
P. 37
26 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
1 .o
0.9
By assuming values of xl, the corresponding y1 may be cal- 0.8
culated.
For hydrocarbon systems, where & = yi/xi, then, 0.7
d
0
%
2 0.6
W
q,r = KdK, = relative volatility (8- 36A) R
I
0.5
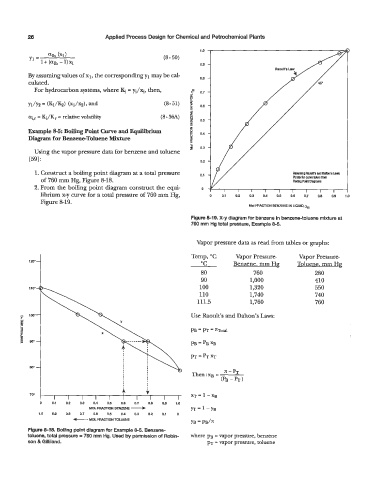
Example 8-5: Boiling Point Curve and Equilibrium z 0.4
9
Diagram for Benzene-Toluene Mixture 5
E
0.3
Using the vapor pressure data for benzene and toluene
[59] : 0.2
1. Construct a boiling point diagram at a total pressure 0.1
of 760 mm Hg, Figure 8-18.
2. From the boiling point diagram construct the equi- 0
librium x-y curve for a total pressure of 760 mm Hg, 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Figure 8-19.
Mol FRACTION BENZENE IN LIQUID, xB
Figure 8-19. X-y diagram for benzene in benzene-toluene mixture at
760 mm Hg total pressure, Example 8-5.
Vapor pressure data as read from tables or graphs:
'"1 Temp, "C Benzene. mm Hg Toluene, mm Hg
Vapor Pressure-
Vapor Pressure-
"C
760
80
280
1,000
90
550
100 1,320 410
110 1,740 '740
111.5 1,760 760
Use Raoult's and Dalton's Laws:
v
70" XT= 1 -XB
I I I I I I I I
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
MOL FRACTION BENZENE
1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0
f--- MOL FRACTION TOLUENE
Figure 8-18. Boiling point diagram for Example 8-5. Benzene-
toluene, total pressure = 760 mm Hg. Used by permission of Robin- where PB = vapor pressure, benzene
son & Gilliland. PT = vapor pressure, toluene