Page 44 - Applied Statistics Using SPSS, STATISTICA, MATLAB and R
P. 44
1.8 Software Tools 23
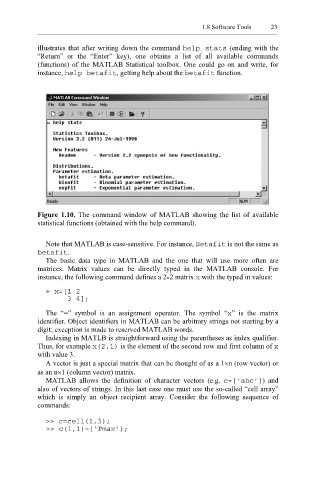
illustrates that after writing down the command help stats (ending with the
“Return” or the “Enter” key), one obtains a list of all available commands
(functions) of the MATLAB Statistical toolbox. One could go on and write, for
instance, p betafit hel , getting help about the betaf it function.
Figure 1.10. The command window of MATLAB showing the list of available
statistical functions (obtained with the help command).
Note that MATLAB is case-sensitive. For instance, Beta fit is not the same as
betafit .
The basic data type in MATLAB and the one that will use more often are
matrices. Matrix values can be directly typed in the MATLAB console. For
instance, the following command defines a 2×2 matrix x with the typed in values:
» x=[1 2
3 4];
”
The “= symbol is an assignment operator. The symbol “x” is the matrix
identifier. Object identifiers in MATLAB can be arbitrary strings not starting by a
digit; exception is made to reserved MATLAB words.
Indexing in MATLB is straightforward using the parentheses as index qualifier.
Thus, for example x(2,1) is the element of the second row and first column of x
with value 3.
A vector is just a special matrix that can be thought of as a 1×n (row vector) or
as an n×1 (column vector) matrix.
MATLAB allows the definition of character vectors (e.g. c=[‘abc’]) and
also of vectors of strings. In this last case one must use the so-called “cell array”
which is simply an object recipient array. Consider the following sequence of
commands:
>> c=cell(1,3);
>> c(1,1)={‘Pmax’};