Page 219 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 219
5B.16 BISMUTH IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: GREEN CHEMISTRY 199
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.24
With appropriate assumptions (about work-up, etc.), explain the formation of an
-acylbismuthonium ion in reaction (5B.95).
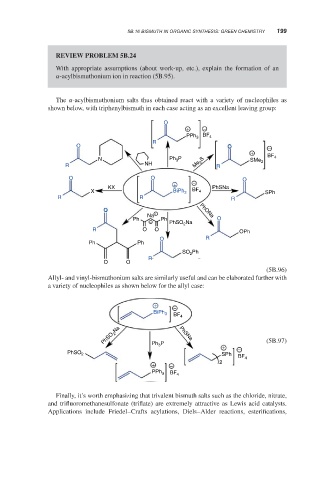
The -acylbismuthonium salts thus obtained react with a variety of nucleophiles as
shown below, with triphenylbismuth in each case acting as an excellent leaving group:
O
+ −
BF
PPh 3 4
R
O O −
+
N Ph P SMe 2 BF 4
3
R NH Me 2 S R
O O O
+ −
KX PhSNa
X BiPh 3 BF 4 SPh
R R R
O PhONa
Na +
Ph Ph O
− PhSO Na
2
R O O OPh
O R
Ph Ph
SO Ph
2
R
O O
(5B.96)
Allyl- and vinyl-bismuthonium salts are similarly useful and can be elaborated further with
a variety of nucleophiles as shown below for the allyl case:
+ −
BiPh 3 BF 4
PhSO 2 Na PhSNa (5B.97)
Ph P
3
+ −
SPh
PhSO 2
BF 4
+ − 2
PPh 3 BF 4
Finally, it’s worth emphasizing that trivalent bismuth salts such as the chloride, nitrate,
and trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate) are extremely attractive as Lewis acid catalysts.
Applications include Friedel–Crafts acylations, Diels–Alder reactions, esterifications,