Page 217 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 217
5B.16 BISMUTH IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: GREEN CHEMISTRY 197
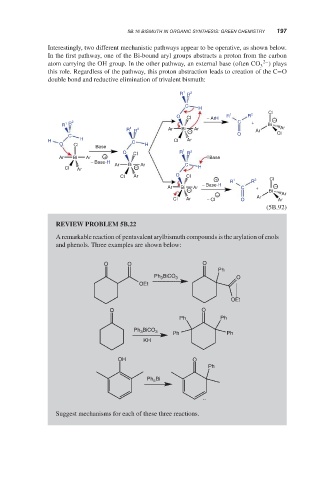
Interestingly, two different mechanistic pathways appear to be operative, as shown below.
In the first pathway, one of the Bi-bound aryl groups abstracts a proton from the carbon
atom carrying the OH group. In the other pathway, an external base (often CO 2– ) plays
3
this role. Regardless of the pathway, this proton abstraction leads to creation of the C=O
double bond and reductive elimination of trivalent bismuth:
1 2
R R
C
H
CI
O CI − ArH R 1 R 2
1 R 2 C + −
R Bi Ar
1
R R 2 Ar Bi − Ar Ar
C O CI
H H CI Ar
O CI C H
Base
1
O CI R R 2
Ar Bi Ar + Base
− Base-H
Ar Bi Ar C
CI Ar − − H
CI Ar O CI
+ R 1 R 2 CI
− Base-H
Ar Bi Ar C + −
− Bi
− Ar
CI Ar − Cl O Ar Ar
(5B.92)
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.22
A remarkable reaction of pentavalent arylbismuth compounds is the arylation of enols
and phenols. Three examples are shown below:
O O O
Ph
Ph 3 BiCO 3 O
OEt
OEt
O O O
Ph Ph
Ph BiCO
3
3
Ph Ph
KH
OH O
Ph
Ph 5 Bi
Suggest mechanisms for each of these three reactions.