Page 212 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 212
THE HEAVIER PNICTOGENS
192
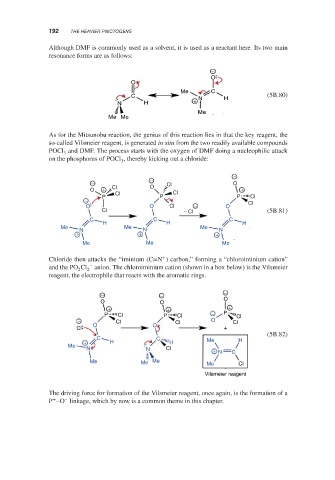
Although DMF is commonly used as a solvent, it is used as a reactant here. Its two main
resonance forms are as follows:
−
O
O
Me C
C N H (5B.80)
N H +
Me
Me Me
As for the Mitsunobu reaction, the genius of this reaction lies in that the key reagent, the
so-called Vilsmeier reagent, is generated in situ from the two readily available compounds
POCl and DMF. The process starts with the oxygen of DMF doing a nucleophilic attack
3
on the phosphorus of POCl , thereby kicking out a chloride:
3
−
− − Cl O
O + Cl O +
Cl Cl
P P P Cl
− Cl
O O Cl − O
Cl − Cl (5B.81)
C C C
H H H H
Me N Me N Me N
+ + +
Me Me Me
+
Chloride then attacks the “iminium (C=N ) carbon,” forming a “chloroiminium cation”
and the PO Cl 2 – anion. The chloroiminium cation (shown in a box below) is the Vilsmeier
2
reagent, the electrophile that reacts with the aromatic rings.
− − −
O O O
+ + +
P Cl P Cl − P Cl
− Cl Cl O Cl
O O
Cl +
(5B.82)
C C
+ H H Me H H
Me
N N Cl
+ N C
Me Me Me Me Cl
Vilsmeier reagent
The driving force for formation of the Vilsmeier reagent, once again, is the formation of a
+ –
P –O linkage, which by now is a common theme in this chapter.