Page 215 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 215
5B.16 BISMUTH IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: GREEN CHEMISTRY 195
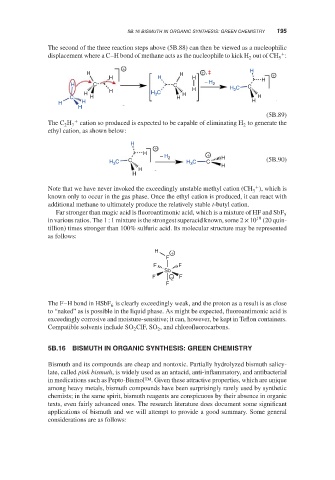
The second of the three reaction steps above (5B.88) can then be viewed as a nucleophilic
+
displacement where a C–H bond of methane acts as the nucleophile to kick H out of CH :
2
5
+
H H + , ‡ H +
H H H H
H C C − H 2 H C C
H H 3
H H 3 C H
C H H H
H H H
H
(5B.89)
The C H + cation so produced is expected to be capable of eliminating H to generate the
2 7 2
ethyl cation, as shown below:
H
+
H +
− H 2 H
H 3 C C H 3 C C (5B.90)
H
H
H
+
Note that we have never invoked the exceedingly unstable methyl cation (CH ), which is
3
known only to occur in the gas phase. Once the ethyl cation is produced, it can react with
additional methane to ultimately produce the relatively stable t-butyl cation.
Far stronger than magic acid is fluoroantimonic acid, which is a mixture of HF and SbF 5
19
in various ratios. The 1 : 1 mixture is the strongest superacid known, some 2 × 10 (20 quin-
tillion) times stronger than 100% sulfuric acid. Its molecular structure may be represented
as follows:
H +
F
F F
Sb
F − F
F
The F–H bond in HSbF is clearly exceedingly weak, and the proton as a result is as close
6
to “naked” as is possible in the liquid phase. As might be expected, fluoroantimonic acid is
exceedingly corrosive and moisture-sensitive; it can, however, be kept in Teflon containers.
Compatible solvents include SO ClF, SO , and chlorofluorocarbons.
2
2
5B.16 BISMUTH IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: GREEN CHEMISTRY
Bismuth and its compounds are cheap and nontoxic. Partially hydrolyzed bismuth salicy-
late, called pink bismuth, is widely used as an antacid, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial
in medications such as Pepto-Bismol™. Given these attractive properties, which are unique
among heavy metals, bismuth compounds have been surprisingly rarely used by synthetic
chemists; in the same spirit, bismuth reagents are conspicuous by their absence in organic
texts, even fairly advanced ones. The research literature does document some significant
applications of bismuth and we will attempt to provide a good summary. Some general
considerations are as follows: