Page 218 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 218
THE HEAVIER PNICTOGENS
198
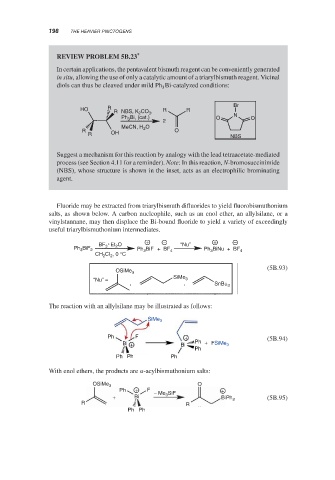
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.23 *
In certain applications, the pentavalent bismuth reagent can be conveniently generated
in situ, allowing the use of only a catalytic amount of a triarylbismuth reagent. Vicinal
diols can thus be cleaved under mild Ph Bi-catalyzed conditions:
3
Br
HO R R NBS, K 2 CO 3 , R R
Ph Bi, (cat.) 2 O N O
3
MeCN, H 2 O
R O
R OH NBS
Suggest a mechanism for this reaction by analogy with the lead tetraacetate-mediated
process (see Section 4.11 for a reminder). Note: In this reaction, N-bromosuccinimide
(NBS), whose structure is shown in the inset, acts as an electrophilic brominating
agent.
Fluoride may be extracted from triarylbismuth difluorides to yield fluorobismuthonium
salts, as shown below. A carbon nucleophile, such as an enol ether, an allylsilane, or a
vinylstannane, may then displace the Bi-bound fluoride to yield a variety of exceedingly
useful triarylbismuthonium intermediates.
+ − + −
BF 3 Et 2 O “Nu”
Ph BiF 2 Ph 3 BiF + BF 4 Ph BiNu + BF 4
3
3
CH CI , 0 °C
2
2
(5B.93)
OSiMe 3
SiMe
“Nu” = 3
, , SnBu 3
The reaction with an allylsilane may be illustrated as follows:
SiMe 3
Ph F + (5B.94)
Bi + Bi Ph + FSiMe 3
Ph
Ph Ph Ph
With enol ethers, the products are -acylbismuthonium salts:
OSiMe 3 O
Ph + F SiF +
+ Bi − Me 3 BiPh 3 (5B.95)
R R
Ph Ph