Page 67 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 67
1.28 SUMMARY 47
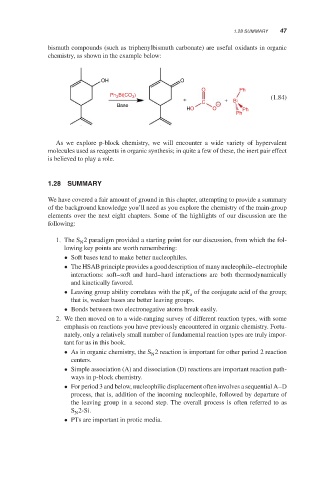
bismuth compounds (such as triphenylbismuth carbonate) are useful oxidants in organic
chemistry, as shown in the example below:
OH O
O Ph
Ph 3 Bi(CO 3 )
+ + Bi (1.84)
Base C −
HO O Ph
Ph
As we explore p-block chemistry, we will encounter a wide variety of hypervalent
molecules used as reagents in organic synthesis; in quite a few of these, the inert pair effect
is believed to play a role.
1.28 SUMMARY
We have covered a fair amount of ground in this chapter, attempting to provide a summary
of the background knowledge you’ll need as you explore the chemistry of the main-group
elements over the next eight chapters. Some of the highlights of our discussion are the
following:
1. The S 2 paradigm provided a starting point for our discussion, from which the fol-
N
lowing key points are worth remembering:
• Soft bases tend to make better nucleophiles.
• The HSAB principle provides a good description of many nucleophile–electrophile
interactions: soft–soft and hard–hard interactions are both thermodynamically
and kinetically favored.
• Leaving group ability correlates with the pK of the conjugate acid of the group;
a
that is, weaker bases are better leaving groups.
• Bonds between two electronegative atoms break easily.
2. We then moved on to a wide-ranging survey of different reaction types, with some
emphasis on reactions you have previously encountered in organic chemistry. Fortu-
nately, only a relatively small number of fundamental reaction types are truly impor-
tant for us in this book.
• As in organic chemistry, the S 2 reaction is important for other period 2 reaction
N
centers.
• Simple association (A) and dissociation (D) reactions are important reaction path-
ways in p-block chemistry.
• For period 3 and below, nucleophilic displacement often involves a sequential A–D
process, that is, addition of the incoming nucleophile, followed by departure of
the leaving group in a second step. The overall process is often referred to as
S 2-Si.
N
• PTs are important in protic media.