Page 231 - Artificial Intelligence for Computational Modeling of the Heart
P. 231
204 Chapter 6 Additional clinical applications
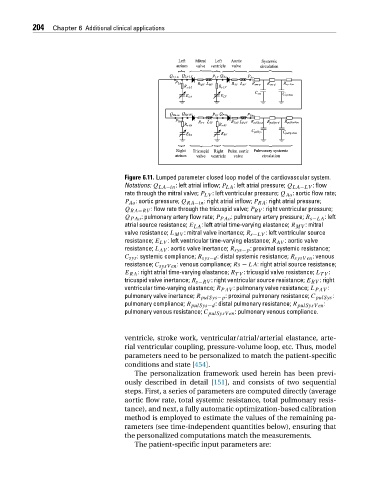
Figure 6.11. Lumped parameter closed loop model of the cardiovascular system.
Notations: Q LA−in : left atrial inflow; P LA :leftatrialpressure; Q LA−LV : flow
rate through the mitral valve; P LV : left ventricular pressure; Q Ao : aortic flow rate;
P Ao : aortic pressure; Q RA−in : right atrial inflow; P RA : right atrial pressure;
Q RA−RV : flow rate through the tricuspid valve; P RV : right ventricular pressure;
Q PAo : pulmonary artery flow rate; P PAo : pulmonary artery pressure; R s−LA :left
atrial source resistance; E LA : left atrial time-varying elastance; R MV :mitral
valve resistance; L MV : mitral valve inertance; R s−LV : left ventricular source
resistance; E LV : left ventricular time-varying elastance; R AV : aortic valve
resistance; L AV : aortic valve inertance; R sys−p : proximal systemic resistance;
C sys : systemic compliance; R sys−d : distal systemic resistance; R sysV en : venous
resistance; C sysV en : venous compliance; Rs − LA: right atrial source resistance;
E RA : right atrial time-varying elastance; R TV : tricuspid valve resistance; L TV :
tricuspid valve inertance; R s−RV : right ventricular source resistance; E RV : right
ventricular time-varying elastance; R PAV : pulmonary valve resistance; L PAV :
pulmonary valve inertance; R pulSys−p : proximal pulmonary resistance; C pulSys :
pulmonary compliance; R pulSys−d : distal pulmonary resistance; R pulSysV en :
pulmonary venous resistance; C pulSysV en : pulmonary venous compliance.
ventricle, stroke work, ventricular/atrial/arterial elastance, arte-
rial ventricular coupling, pressure-volume loop, etc. Thus, model
parameters need to be personalized to match the patient-specific
conditions and state [454].
The personalization framework used herein has been previ-
ously described in detail [151], and consists of two sequential
steps. First, a series of parameters are computed directly (average
aortic flow rate, total systemic resistance, total pulmonary resis-
tance), and next, a fully automatic optimization-based calibration
method is employed to estimate the values of the remaining pa-
rameters (see time-independent quantities below), ensuring that
the personalized computations match the measurements.
The patient-specific input parameters are: