Page 228 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 228
2
212 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
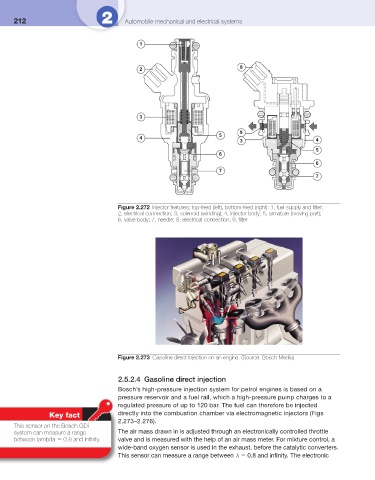
1
8
2
3
9
5
4
3 4
5
6
6
7
7
Figure 2.272 Injector features; top-feed (left), bottom-feed (right): 1, fuel supply and fi lter;
2, electrical connection; 3, solenoid (winding); 4, injector body; 5, armature (moving part);
6, valve body; 7, needle; 8, electrical connection; 9, fi lter
Figure 2.273 Gasoline direct injection on an engine. (Source: Bosch Media)
2.5.2.4 Gasoline direct injection
Bosch’s high-pressure injection system for petrol engines is based on a
pressure reservoir and a fuel rail, which a high-pressure pump charges to a
regulated pressure of up to 120 bar. The fuel can therefore be injected
Key fact directly into the combustion chamber via electromagnetic injectors ( Figs
2.273–2.276 ).
This sensor on the Bosch GDi
system can measure a range The air mass drawn in is adjusted through an electronically controlled throttle
between lambda 0.8 and infi nity. valve and is measured with the help of an air mass meter. For mixture control, a
wide-band oxygen sensor is used in the exhaust, before the catalytic converters.
This sensor can measure a range between λ 0.8 and infi nity. The electronic