Page 289 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 289
CHAP TER 1 0. 1 Tyres and wheels
Wheel rim diameter in inches 12 13 14 15 16 17
Brake disc outer diameter in mm 221 256 278 308 330 360
Brake drum inner diameter in mm 200 230 250 280 300 325
Fig. 10.1-10 The flatter the tyre, i.e. the larger the rim diameter d (Fig. 10.1-1) in comparison with the outside diameter OD T , the larger the
brake discs or drums that can be accommodated, with the advantage of a better braking capacity and less tendency to fade. An
asymmetric well-base rim is favourable (Figs. 8.1-8 and 10.1-11).
The following should be noted for VR tyres: 10.1.2.5.3 Designation of light commercial
over 210 km h –1 and up to 220 km h inclusive, the vehicle tyres
load may only be 90% of the otherwise authorized Tyres for light commercial vehicles have a reinforced
value; substructure compared with those for passenger cars
over 220 km h –1 the carrying capacity reduces by at (Fig. 10.1-5), so they can take higher pressures, which
least 5% per 10 km h –1 speed increment. means they have a higher load capacity. The suffix ‘C’
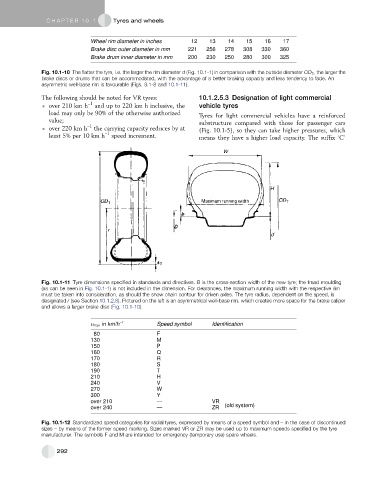
Fig. 10.1-11 Tyre dimensions specified in standards and directives. B is the cross-section width of the new tyre; the tread moulding
(as can be seen in Fig. 10.1-1) is not included in the dimension. For clearances, the maximum running width with the respective rim
must be taken into consideration, as should the snow chain contour for driven axles. The tyre radius, dependent on the speed, is
designated r (see Section 10.1.2.8). Pictured on the left is an asymmetrical well-base rim, which creates more space for the brake caliper
and allows a larger brake disc (Fig. 10.1-10).
max in km/h –1 Speed symbol Identification
80 F
130 M
150 P
160 Q
170 R
180 S
190 T
210 H
240 V
270 W
300 Y
over 210 — VR
over 240 — ZR (old system)
Fig. 10.1-12 Standardized speed categories for radial tyres, expressed by means of a speed symbol and – in the case of discontinued
sizes – by means of the former speed marking. Sizes marked VR or ZR may be used up to maximum speeds specified by the tyre
manufacturer. The symbols F and M are intended for emergency (temporary use) spare wheels.
292