Page 286 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 286
Tyres and wheels C HAPTER 10.1
10.1.2.3 Tubeless or tubed
In passenger cars, the tubeless tyre has almost com-
pletely ousted the tubed tyre. The main reasons are that
the tubeless tyre is:
easier and faster to fit
the inner lining is able to self-seal small incisions
in the tyre.
In tubeless tyres the inner lining performs the function of
the tube, i.e. it prevents air escaping from the tyre. As it
DIN l Diameter d
forms a unit with the carcass and (unlike the tube) is not
43 GS 11.5 43 15.2 under tensional stress, if the tyre is damaged the incision
does not increase in size, rapidly causing loss of pressure
43 GS 16 43 19.5
and failure of the tyre. The use of tubeless tyres is linked
to two conditions:
Fig. 10.1-6 Snap-in rubber valve for tubeless tyres, can be used
on rims with the standard valve holes of 11.5 mm and 16 mm safety contour on the rim (Fig. 10.1-21)
diameter. The numerical value 43 gives the total length in mm its air-tightness.
(dimension l ). There is also the longer 49 GS 11.5 design.
Because this is not yet guaranteed worldwide, tubed
tyres continue to be fitted in some countries. When
choosing the tube, attention should be paid to ensuring
the correct type for the tyre. If the tube is too big it will
crease, and if it is too small it will be overstretched, both
of which reduce durability. In order to avoid confusion,
the tyres carry the following marking on the sidewall:
tubeless (Fig. 10.1-18, point 3)
tubed or tube type.
Valve specification d
38/11.5 11.7
38/16 16.5
Fig. 10.1-7 Rubber valve vulcanized onto tubes. Designations
are 38/11.5 or 38/16.
susceptibility of the thinner sidewalls of the tyres to
damage compared with diagonal ply tyres. The advan-
tages over cross-ply tyres, which are especially important
for today’s passenger cars and commercial vehicles, are:
significantly higher mileage
greater load capacity at lower component weight
lower rolling resistance
better aquaplaning properties
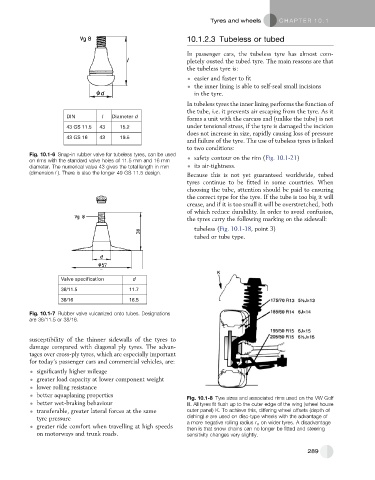
Fig. 10.1-8 Tyre sizes and associated rims used on the VW Golf
better wet-braking behaviour III. All tyres fit flush up to the outer edge of the wing (wheel house
transferable, greater lateral forces at the same outer panel) K. To achieve this, differing wheel offsets (depth of
tyre pressure dishing) e are used on disc-type wheels with the advantage of
a more negative rolling radius r s on wider tyres. A disadvantage
greater ride comfort when travelling at high speeds then is that snow chains can no longer be fitted and steering
on motorways and trunk roads. sensitivity changes very slightly.
289