Page 423 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 423
CHAP TER 1 4. 1 Global positioning technology
application developers who want to integrate GPS into possible to execute DR or WAAS algorithms on the same
their designs, but cannot afford the cost or space neces- processor as the GPS algorithms, further improving the
sary for a board-level solution. accuracy of the positioning solution at little or no increase
in chip set cost.
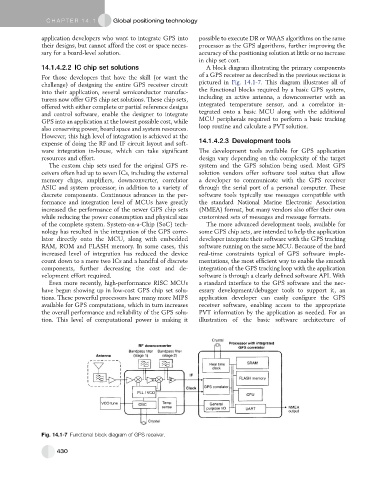
14.1.4.2.2 IC chip set solutions A block diagram illustrating the primary components
of a GPS receiver as described in the previous sections is
For those developers that have the skill (or want the
pictured in Fig. 14.1-7. This diagram illustrates all of
challenge) of designing the entire GPS receiver circuit
the functional blocks required by a basic GPS system,
into their application, several semiconductor manufac-
including an active antenna, a downconverter with an
turers now offer GPS chip set solutions. These chip sets,
offered with either complete or partial reference designs integrated temperature sensor, and a correlator in-
and control software, enable the designer to integrate tegrated onto a basic MCU along with the additional
GPS into an application at the lowest possible cost, while MCU peripherals required to perform a basic tracking
also conserving power, board space and system resources. loop routine and calculate a PVT solution.
However, this high level of integration is achieved at the
expense of doing the RF and IF circuit layout and soft- 14.1.4.2.3 Development tools
ware integration in-house, which can take significant The development tools available for GPS application
resources and effort. design vary depending on the complexity of the target
The custom chip sets used for the original GPS re- system and the GPS solution being used. Most GPS
ceivers often had up to seven ICs, including the external solution vendors offer software tool suites that allow
memory chips, amplifiers, downconverter, correlator a developer to communicate with the GPS receiver
ASIC and system processor, in addition to a variety of through the serial port of a personal computer. These
discrete components. Continuous advances in the per- software tools typically use messages compatible with
formance and integration level of MCUs have greatly the standard National Marine Electronic Association
increased the performance of the newer GPS chip sets (NMEA) format, but many vendors also offer their own
while reducing the power consumption and physical size customized sets of messages and message formats.
of the complete system. System-on-a-Chip (SoC) tech- The more advanced development tools, available for
nology has resulted in the integration of the GPS corre- some GPS chip sets, are intended to help the application
lator directly onto the MCU, along with embedded developer integrate their software with the GPS tracking
RAM, ROM and FLASH memory. In some cases, this software running on the same MCU. Because of the hard
increased level of integration has reduced the device real-time constraints typical of GPS software imple-
count down to a mere two ICs and a handful of discrete mentations, the most efficient way to enable the smooth
components, further decreasing the cost and de- integration of the GPS tracking loop with the application
velopment effort required. software is through a clearly defined software API. With
Even more recently, high-performance RISC MCUs a standard interface to the GPS software and the nec-
have begun showing up in low-cost GPS chip set solu- essary development/debugger tools to support it, an
tions. These powerful processors have many more MIPS application developer can easily configure the GPS
available for GPS computations, which in turn increases receiver software, enabling access to the appropriate
the overall performance and reliability of the GPS solu- PVT information by the application as needed. For an
tion. This level of computational power is making it illustration of the basic software architecture of
Fig. 14.1-7 Functional block diagram of GPS receiver.
430