Page 568 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 568
Vehicle safety C HAPTER 17.1
USA, failure of drivers to fasten seat belts has been the Driver’s seat
Spring Igniter
cause of serious injuries, which has led, unjustifiably, to bag
Direction Weight
doubts being expressed regarding the effectiveness of air of impact
bags.
For the protection of front seat passengers, air bags Nitrogen
are installed behind a panel in the dash fascia, and side
Firing pin
air bags may be embodied in the seat squabs. An ad- Mechanical sensor Inflator
vantage of the latter site is that it moves with the seat
when its position is adjusted, so the bag can be smaller
Air bag for driver
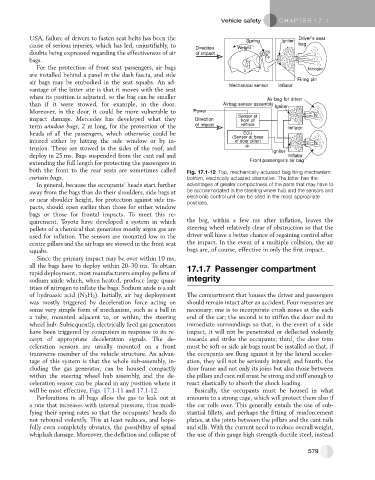
than if it were stowed, for example, in the door. Airbag sensor assembly Igniter
Moreover, in the door, it could be more vulnerable to Power
Sensor at N
impact damage. Mercedes has developed what they Direction front of
term window bags, 2 m long, for the protection of the of impact vehicle Inflator
heads of all the passengers, which otherwise could be ECU
(Sensor at base
injured either by hitting the side window or by in- of door pillar) N
trusion. These are stowed in the sides of the roof, and Igniter
deploy in 25 ms. Bags suspended from the cant rail and Inflator
extending the full length for protecting the passengers in Front passenger’s air bag
both the front to the rear seats are sometimes called Fig. 17.1-12 Top, mechanically actuated bag firing mechanism:
curtain bags. bottom, electrically actuated alternative. The latter has the
In general, because the occupants’ heads start further advantages of greater compactness of the parts that may have to
away from the bags than do their shoulders, side bags at be accommodated in the steering wheel hub and the sensors and
or near shoulder height, for protection against side im- electronic control unit can be sited in the most appropriate
positions.
pacts, should open earlier than those for either window
bags or those for frontal impacts. To meet this re-
quirement, Toyota have developed a system in which the bag, within a few ms after inflation, leaves the
pellets of a chemical that generates mostly argon gas are steering wheel relatively clear of obstruction so that the
used for inflation. The sensors are mounted low in the driver will have a better chance of regaining control after
centre pillars and the air bags are stowed in the front seat the impact. In the event of a multiple collision, the air
squabs. bags are, of course, effective in only the first impact.
Since the primary impact may be over within 10 ms,
all the bags have to deploy within 20–30 ms. To obtain 17.1.7 Passenger compartment
rapid deployment, most manufacturers employ pellets of
sodium azide which, when heated, produce large quan- integrity
tities of nitrogen to inflate the bags. Sodium azide is a salt
of hydroazic acid (N 3 H 3 ). Initially, air bag deployment The compartment that houses the driver and passengers
was mostly triggered by deceleration force acting on should remain intact after an accident. Four measures are
some very simple form of mechanism, such as a ball in necessary: one is to incorporate crush zones at the each
a tube, mounted adjacent to, or within, the steering end of the car; the second is to stiffen the door and its
wheel hub. Subsequently, electrically fired gas generators immediate surroundings so that, in the event of a side
have been triggered by computers in response to its re- impact, it will not be penetrated or deflected violently
ceipt of appropriate deceleration signals. The de- inwards and strike the occupants; third, the door trim
celeration sensors are usually mounted on a front must be soft or side air bags must be installed so that, if
transverse member of the vehicle structure. An advan- the occupants are flung against it by the lateral acceler-
tage of this system is that the whole sub-assembly, in- ation, they will not be seriously injured; and fourth, the
cluding the gas generator, can be housed compactly door frame and not only its joins but also those between
within the steering wheel hub assembly, and the de- the pillars and cant rail must be strong and stiff enough to
celeration sensor can be placed in any position where it react elastically to absorb the shock loading.
will be most effective, Figs. 17.1-11 and 17.1-12. Basically, the occupants must be housed in what
Perforations in all bags allow the gas to leak out at amounts to a strong cage, which will protect them also if
a rate that increases with internal pressure, thus modi- the car rolls over. This generally entails the use of sub-
fying their spring rates so that the occupants’ heads do stantial fillets, and perhaps the fitting of reinforcement
not rebound violently. This at least reduces, and hope- plates, at the joints between the pillars and the cant rails
fully even completely obviates, the possibility of spinal and sills. With the current need to reduce overall weight,
whiplash damage. Moreover, the deflation and collapse of the use of thin gauge high strength ductile steel, instead
579