Page 572 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 572
Vehicle safety C HAPTER 17.1
in the event of air bag deployment. It therefore could
Belt
become desirable to mount the pedals on a base plate web
that could be moved horizontally to adjust its position
relative to the seat. This, together with the usual seat
adjustment facility, would give the driver the means of
Belt reel
positioning himself optimally in the horizontal sense
relative to his steering wheel and other controls. Vertical
adjustment of either the steering wheel or seat might also
be desirable, however.
17.1.11 Seat belts
Ideally everyone would have a safety harness of the two
shoulder strap (four point) type, worn by aircraft pilots
and rally drivers. However, this is commonly regarded as
too restrictive to be acceptable by the motoring public. It Gas at high
is also more costly than the adjustable combined lap and pressure
single shoulder strap (three point) type harness. The Pretensioner
latter type is satisfactory if the lap belt fits snugly round cable
the pelvis, the upper anchorage for the shoulder strap
Plunger
is low enough to prevent strangulation or damage to
the neck of the person it is supposed to protect, the
whole harness is a reasonably close fit around the body,
and the occupant can instantly release himself from it in
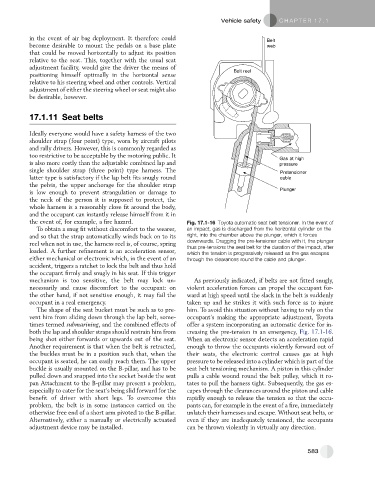
the event of, for example, a fire hazard. Fig. 17.1-16 Toyota automatic seat belt tensioner. In the event of
To obtain a snug fit without discomfort to the wearer, an impact, gas is discharged from the horizontal cylinder on the
and so that the strap automatically winds back on to its right, into the chamber above the plunger, which it forces
downwards. Dragging the pre-tensioner cable with it, the plunger
reel when not in use, the harness reel is, of course, spring thus pre-tensions the seat belt for the duration of the impact, after
loaded. A further refinement is an acceleration sensor, which the tension is progressively released as the gas escapes
either mechanical or electronic which, in the event of an through the clearances round the cable and plunger.
accident, triggers a ratchet to lock the belt and thus hold
the occupant firmly and snugly in his seat. If this trigger
mechanism is too sensitive, the belt may lock un- As previously indicated, if belts are not fitted snugly,
necessarily and cause discomfort to the occupant: on violent acceleration forces can propel the occupant for-
the other hand, if not sensitive enough, it may fail the ward at high speed until the slack in the belt is suddenly
occupant in a real emergency. taken up and he strikes it with such force as to injure
The shape of the seat bucket must be such as to pre- him. To avoid this situation without having to rely on the
vent him from sliding down through the lap belt, some- occupant’s making the appropriate adjustment, Toyota
times termed submarining, and the combined effects of offer a system incorporating an automatic device for in-
both the lap and shoulder straps should restrain him from creasing the pre-tension in an emergency, Fig. 17.1-16.
being shot either forwards or upwards out of the seat. When an electronic sensor detects an acceleration rapid
Another requirement is that when the belt is retracted, enough to throw the occupants violently forward out of
the buckles must be in a position such that, when the their seats, the electronic control causes gas at high
occupant is seated, he can easily reach them. The upper pressure to be released into a cylinder which is part of the
buckle is usually mounted on the B-pillar, and has to be seat belt tensioning mechanism. A piston in this cylinder
pulled down and snapped into the socket beside the seat pulls a cable wound round the belt pulley, which it ro-
pan Attachment to the B-pillar may present a problem, tates to pull the harness tight. Subsequently, the gas es-
especially to cater for the seat’s being slid forward for the capes through the clearances around the piston and cable
benefit of driver with short legs. To overcome this rapidly enough to release the tension so that the occu-
problem, the belt is in some instances carried on the pants can, for example in the event of a fire, immediately
otherwise free end of a short arm pivoted to the B-pillar. unlatch their harnesses and escape. Without seat belts, or
Alternatively, either a manually or electrically actuated even if they are inadequately tensioned, the occupants
adjustment device may be installed. can be thrown violently in virtually any direction.
583