Page 793 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 793
CHAP TER 2 3. 1 Automotive instrumentation and telematics
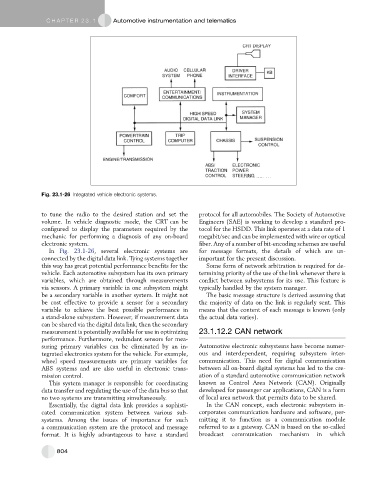
Fig. 23.1-26 Integrated vehicle electronic systems.
to tune the radio to the desired station and set the protocol for all automobiles. The Society of Automotive
volume. In vehicle diagnostic mode, the CRT can be Engineers (SAE) is working to develop a standard pro-
configured to display the parameters required by the tocol for the HSDD. This link operates at a data rate of 1
mechanic for performing a diagnosis of any on-board megabit/sec and can be implemented with wire or optical
electronic system. fiber. Any of a number of bit-encoding schemes are useful
In Fig. 23.1-26, several electronic systems are for message formats, the details of which are un-
connected by the digital data link. Tying systems together important for the present discussion.
this way has great potential performance benefits for the Some form of network arbitration is required for de-
vehicle. Each automotive subsystem has its own primary termining priority of the use of the link whenever there is
variables, which are obtained through measurements conflict between subsystems for its use. This feature is
via sensors. A primary variable in one subsystem might typically handled by the system manager.
be a secondary variable in another system. It might not The basic message structure is derived assuming that
be cost effective to provide a sensor for a secondary the majority of data on the link is regularly sent. This
variable to achieve the best possible performance in means that the content of each message is known (only
a stand-alone subsystem. However, if measurement data the actual data varies).
can be shared via the digital data link, then the secondary
measurement is potentially available for use in optimizing 23.1.12.2 CAN network
performance. Furthermore, redundant sensors for mea-
suring primary variables can be eliminated by an in- Automotive electronic subsystems have become numer-
tegrated electronics system for the vehicle. For example, ous and interdependent, requiring subsystem inter-
wheel speed measurements are primary variables for communication. This need for digital communication
ABS systems and are also useful in electronic trans- between all on-board digital systems has led to the cre-
mission control. ation of a standard automotive communication network
This system manager is responsible for coordinating known as Control Area Network (CAN). Originally
data transfer and regulating the use of the data bus so that developed for passenger car applications, CAN is a form
no two systems are transmitting simultaneously. of local area network that permits data to be shared.
Essentially, the digital data link provides a sophisti- In the CAN concept, each electronic subsystem in-
cated communication system between various sub- corporates communication hardware and software, per-
systems. Among the issues of importance for such mitting it to function as a communication module
a communication system are the protocol and message referred to as a gateway. CAN is based on the so-called
format. It is highly advantageous to have a standard broadcast communication mechanism in which
804