Page 45 - Automotive Engineering
P. 45
CH AP TER 2 .1 Measurement of torque, power, speed and fuel consumption
Torque
M mean
0 180° 360° 540° 720°
Crank angle
½-order
1-order
1½-order
2-order
2½-order
3-order
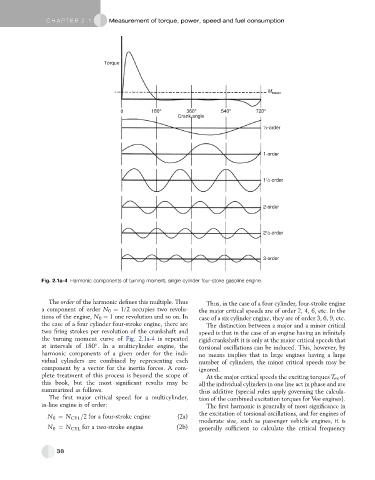
Fig. 2.1a-4 Harmonic components of turning moment, single cylinder four-stoke gasoline engine.
The order of the harmonic defines this multiple. Thus Thus, in the case of a four cylinder, four-stroke engine
a component of order N 0 ¼ 1/2 occupies two revolu- the major critical speeds are of order 2, 4, 6, etc. In the
tions of the engine, N 0 ¼ 1 one revolution and so on. In case of a six cylinder engine, they are of order 3, 6, 9, etc.
the case of a four cylinder four-stroke engine, there are The distinction between a major and a minor critical
two firing strokes per revolution of the crankshaft and speed is that in the case of an engine having an infinitely
the turning moment curve of Fig. 2.1a-4 is repeated rigid crankshaft it is only at the major critical speeds that
at intervals of 180 . In a multicylinder engine, the torsional oscillations can be induced. This, however, by
harmonic components of a given order for the indi- no means implies that in large engines having a large
vidual cylinders are combined by representing each number of cylinders, the minor critical speeds may be
component by a vector for the inertia forces. A com- ignored.
plete treatment of this process is beyond the scope of At the major critical speeds the exciting torques T ex of
this book, but the most significant results may be all the individual cylinders in one line act in phase and are
summarized as follows. thus additive (special rules apply governing the calcula-
The first major critical speed for a multicylinder, tion of the combined excitation torques for Vee engines).
in-line engine is of order: The first harmonic is generally of most significance in
the excitation of torsional oscillations, and for engines of
N 0 ¼ N CYL =2 for a four-stroke engine (2a)
moderate size, such as passenger vehicle engines, it is
N 0 ¼ N CYL for a two-stroke engine (2b) generally sufficient to calculate the critical frequency
38