Page 103 - Basics of Fluid Mechanics and Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
P. 103
88 BASICS OF FLUID MECHANICS AND INTRODUCTION TO CFD
the source from the element ds; located at (rj, 4;) on that panel. Here
riz = V (x; — 23)? + (yi — y;)* is the distance from the control point
(xz, 4) to an arbitrary point (z;,y;) on the j-th panel.
The velocity potential for the flow obtained by superposition of the
given uniform flow and the m source panels is then
m
AG
®(z;, y;) = Ua;t+ > x / Inrizds;.
j=1
Let now (z;,y;) be the control point on the i-th panel, where the
outward normal n; makes an angle 6; with the uniform stream. At this
point on the surface of the body, the above slip condition becomes
xi Aj
.
>t > ) Oa Ua = —U cos j,i = 1,...,m
(2.10)
T#i
where
ly =
d Inr;;ds,
ij = y dng
95 -
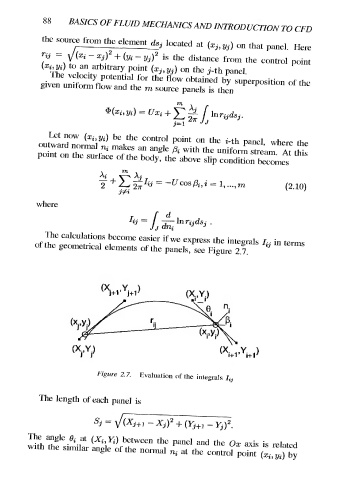
The calculations become easier if we express the integrals I;; in terms
of the geometrical elements of the panels, see Figure 2.7.
OY” (%Y)
(%, Y)
(Xi Via
Figure 2.7.
Evaluation of the integrals J;,
The length of each panel is
Sj = VXju1 ~ Xj)? + (Yj — Yj)”.
The angle 6; at (Xj, ¥i) between the panel and the Oz axis is related
with the similar angle of the normal n; at the control point (x3, yi) by