Page 292 - Battery Reference Book
P. 292
Lithium (aluminium) iron sulphide secondary cells 24/15
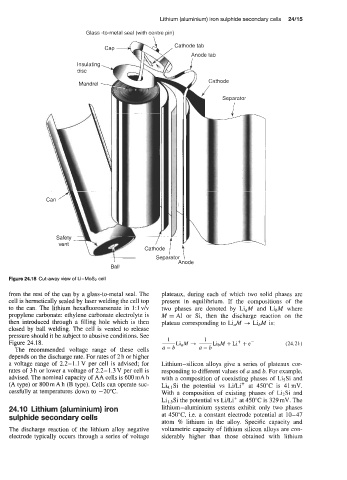
Glass -to-metal seal (with centre pin)
\
disc >
Insulating
7 / Separator
Mandrel Cathode
F' Cathode I \
Sepa;ator I
Ball Anode
Figure 24.18 Cut-away view of Li-MoS2 cell
from the rest of the can by a glass-to-metal seal. The plateaux, during each of which two solid phases are
cell is hermetically sealed by laser welding the cell top present in equilibrium. If the compositions of the
to the can. The lithium hexafluoroarsenate in 1: 1 v/v two phases are denoted by LiaM and LibM where
propylene carbonate: ethylene carbonate electrolyte is M = A1 or Si, then the discharge reaction on the
then introduced through a filling hole which is then plateau corresponding to Li,M --+ LibM is:
closed by ball welding. The cell is vented to release
pressure should it be subject to abusive conditions. See
1
Figure 24.18. -LiaM + ~ 1 LibM + Li+ + e- (24.21)
The recommended voltage range of these cells a-b a-b
depends on the discharge rate. For rates of 2 h or higher
a voltage range of 2.2-1.1 V per cell is advised; for Lithium-silicon alloys give a series of plateaux cor-
rates of 3 h or lower a voltage of 2.2- 1.3 V per cell is responding to different values of a and b. For example,
advised. The nominal capacity of AA cells is 600 mA h with a composition of coexisting phases of LisSi and
(A type) or 800 m A h (B type). Cells can operate suc- L&Si the potential vs Li/Li+ at 450°C is 41mV.
cessfully at temperatures down to -20°C. With a composition of existing phases of Li2Si and
Li&i the potential vs Li/Li+ at 450°C is 329mV. The
24.10 Lithium (aluminium) iron lithium-aluminium systems exhibit only two phases
sulphide secondary cells at 450"C, i.e. a constant electrode potential at 10-47
atom % lithium in the alloy. Specific capacity and
The discharge reaction of the lithium alloy negative voltametric capacity of lithium silicon alloys are con-
electrode typically occurs through a series of voltage siderably higher than those obtained with lithium