Page 308 - Battery Reference Book
P. 308
Calcium anode-based thermal batteries 27/5
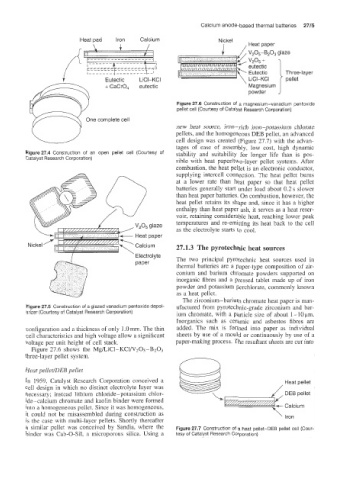
I , Heat paper
V205-B203 glaze
v2°5 +
eutectic
Eutectic Three-layer
LiCI-KCI I pellet
+ CaCrO, eutectic ' Magnesium J
powder
Figure 27.6 Construction of a magnesium-vanadium pentoxide
pellet cell (Courtesy of Catalyst Research Corporation)
One complete cell
new heat source, iron-rich iron-potassium chlorate
pellets, and the homogeneous DEB pellet, an advanced
cell design was created (Figure 27.7) with the advan-
tages of ease of assembly, low cost, high dynamic
Figure 27.4 Consrruction of an open pellet cell (Courtesy of stability and suitability for longer life than is pos-
Catalyst Research Corporation) sible with heat paper/two-layer pellet systems. After
combustion, the heat pellet is an electronic conductor,
supplying intercell connection. The heat pellet burns
at a lower rate than heat paper so that heat pellet
batteries generally start under load about 0.2 s slower
than heat paper batteries. On combustion, however, the
heat pellet retains its shape and, since it has a higher
enthalpy than heat paper ash, it serves as a heat reser-
voir, retaining considerable heat, reaching lower peak
temperatures and re-emitting its heat back to the cell
as the electrolyte starts to cool.
27.1.3 The pyrotechnic heat sources
The two principal pyrotechnic heat sources used in
thermal batteries are a paper-type composition of zir-
conium and barium chromate powders supported on
inorganic fibres and a pressed tablet made up of iron
powder and potassium perchlorate, commonly known
as a heat pellet.
The zirconium-barium chromate heat paper is man-
Figure 27.5 Construction of a glazed vanadium pentoxide depol- ufactured from pyrotechnic-grade zirconium and bar-
arizer (Courtesy of Catalyst Research Corporation) ium chromate, with a particle size of about l-lOpm.
Inorganics such as ceramic and asbestos fibres are
configuration and a thickness of only 1 .O mm. The thin added. The mix is formed into paper as individual
cell characteristics and high voltage allow a significant sheets by use of a mould or continuously by use of a
voltage per unit height of cell stack. paper-making process. The resultant sheets are cut into
Figure 27.6 shows the Mg/LiCl-KCW205-B203
three-layer pellet system.
Heat pellet/DEB pellet
In 1959, Catalyst Research Corporation conceived a
cell design in which no distinct electrolyte layer was
necessary; instead lithium chloride-potassium chlor- L
ide-calcium chromate and kaolin binder were formed
Salciun
into a homogeneous pellet. Since it was homogeneous, '
it could not be misassembled during construction as Iron
is the case with multi-layer pellets. Shortly thereafter
a similar pellet was conceived by Sandia, where the Figure 27.7 Construction of a heat pellet-DEB pellet cell (Cour-
binder was Cab-0-Sil, a microporous silica. Using a tesy of Catalyst Research Corporation)