Page 175 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 175
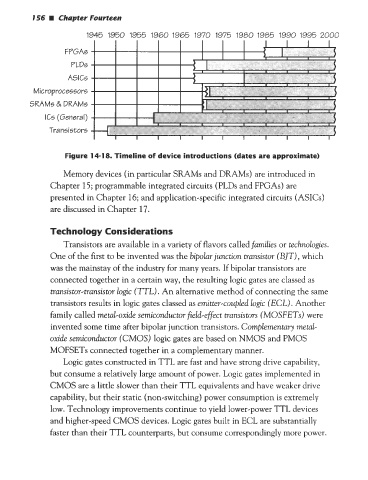
156 Chapter Fourteen
1945 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970 1975 1900 1905 1990 1995 2000
FPGAs
PLDs
A5ICs
Microprocessors
SRAMs & DRAM5
ICs (General)
Transistors
Figure 14-1 8. Timeline of device introductions (dates are approximate)
Memory devices (in particular SRAMs and DRAMS) are introduced in
Chapter 15; programmable integrated circuits (PLDs and FPGAs) are
presented in Chapter 16; and application-specific integrated circuits ( ASICs)
are discussed in Chapter 17.
Technology Considerations
Transistors are available in a variety of flavors called families or technologies.
One of the first to be invented was the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) , which
was the mainstay of the industry for many years. If bipolar transistors are
connected together in a certain way, the resulting logic gates are classed as
transistor-transistor logic (TTL). An alternative method of connecting the same
transistors results in logic gates classed as emitter-coupled logic (ECL). Another
family called metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) were
invented some time after bipolar junction transistors. Complementary metal-
oxide semiconductor (CMOS) logic gates are based on NMOS and PMOS
MOFSETs connected together in a complementary manner.
Logic gates constructed in TTL are fast and have strong drive capability,
but consume a relatively large amount of power. Logic gates implemented in
CMOS are a little slower than their TTL equivalents and have weaker drive
capability, but their static (non-switching) power consumption is extremely
low. Technology improvements continue to yield lower-power TTL devices
and higher-speed CMOS devices. Logic gates built in ECL are substantially
faster than their TTL counterparts, but consume correspondingly more power.