Page 176 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 176
Fatigue Limit of Ductile Metals Under Multiaxial Loading 161
stress alternate without mean stresses are not considered in the statistical evaluation. As is
shown in Fig. 3, the prediction according to SM with the elliptic equation is very good for this
simple load case.
For each load case, the SIH provides a good prediction of the fatigue limits. The average
values X are still near the unity and the standard deviations s are small. A greater scatter is
estimated only for the load case where one shear stress alternates with a,, oym or zVm, and
for the load case where two normal stresses alternate with phase difference and mean stresses
different from zero.
The statistical distribution of the ratio x for all 182 test results is plotted in Fig. 13. For the
cases considered, the further-developed shear stress intensity hypothesis SIH provides an
accurate prediction of the fatigue limit. The ratio x of the experimental fatigue limit to the
calculated fatigue limit has an average value equal to about 1.0, and ranges between 0.8 and
1.2. With these results, 90 per cent of the values are within the range between 0.85 and 1.1. The
standard deviation s is equal to 0.067.
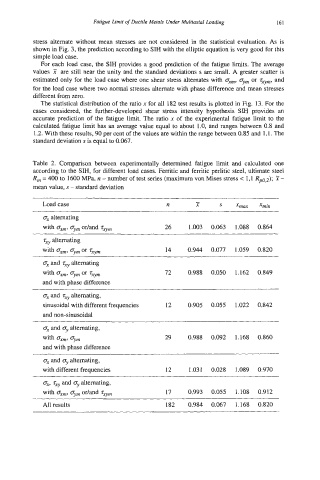
Table 2. Comparison between experimentally determined fatigue limit and calculated one
according to the SIH, for different load cases. Femtic and ferritic perlitic steel, ultimate steel
Rm = 400 to 1600 MPa, n - number of test series (maximum von Mises stress < 1,l Rpo,2); 3E -
mean value, s - standard deviation
Load case n 7 S xmax Xmin
ox alternating
with om, oym orland zxym 26 1.003 0.063 1.088 0.864
zxy alternating
with oXm, oym or rxym 14 0.944 0.077 1.059 0.820
ox and zxy alternating
with ox,, or,,, or zVm 72 0.988 0.050 1.162 0.849
and with phase difference
~~~~~~~ ~~~
ox and zxy alternating,
sinusoidal with different frequencies 12 0.905 0.055 1.022 0.842
and non-sinusoidal
ox and oy alternating,
with ox,,,, oYm 29 0.988 0.092 1.168 0.860
and with phase difference
ox and or alternating,
with different frequencies I2 1.031 0.028 1.089 0.970
ox, zq and cy alternating,
with o,,, oVm orland z,, 17 0.993 0.055 1.108 0.912
All results 182 0.984 0.067 1.168 0.820