Page 265 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 265
The Multiaxial Fatigue Strength of Specimens Containing Small Defects 249
be predicted using Eq.(3) without the need for a fatigue test. In addition, the value of 4 can be
estimated by stress analysis, as verified by Beretta and Muakami [21,22]. If the average value
4 calculated by Beretta and Murakami is used, ie., 0.85, &.(lo) becomes:
1.38(rJaW)’ + 0.176(aJq$ + 0.824(aJow) = 1 (1 1)
This expression is considered to be applicable to specimens containing a round defect on or
near the surface where plane stress condition is satisfied. The use of this expression will be
demonstrated in the following.
MATERIALS AND EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
The materials investigated in this study are: steels, nodular cast irons and a high strength brass.
Although experimental data for an annealed steel and the cast irons have previously reported
elsewhere [23,24], they will be included below for purposes of discussion. The chemical
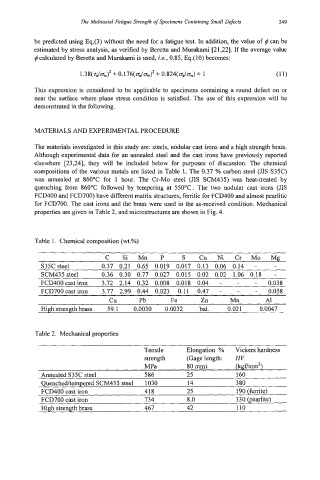
compositions of the various metals are listed in Table 1. The 0.37 YO carbon steel (JIS S35C)
was annealed at 860°C for 1 hour. The Cr-Mo steel (JIS SCM435) was heat-treated by
quenching from 860°C followed by tempering at 550°C. The two nodular cast irons (JIS
FCD400 and FCD700) have different matrix structures; ferritic for FCD4OO and almost pearlitic
for FCD700. The cast irons and the brass were used in the as-received condition. Mechanical
properties are given in Table 2, and microstructures are shown in Fig. 4.
Table 1. Chemical composition (wt.%)
C Si Mn P S Cu Ni Cr Mo Mg
S35C steel 0.37 0.21 0.65 0.019 0.017 0.13 0.06 0.14 -
SCM435 steel 0.36 0.30 0.77 0.027 0.015 0.02 0.02 1.06 0.18 -
FCD400castiron 3.72 2.14 0.32 0.008 0.018 0.04 - - 0.038
FCD700 cast iron 3.77 2.99 0.44 0.023 0.11 0.47 - - 0.058
cu Pb Fe Zn Mn A1
High strength brass 59.1 0.0030 0.0032 bal. 0.02 1 0.0047
Table 2. Mechanical properties
Tensile Elongation % Vickers hardness
strength (Gage length: HV
MPa 80 mm) ( kgf/mm2)
Annealed S35C steel 586 25 160
Quenchedkempered SCM435 steel 1030 14 380
FCD400 cast iron 418 25 190 (femte)
FCD700 cast iron 734 8.0 330 (pearlite)
High strength brass 467 42 110