Page 307 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 307
The Background of Fatigue Limit Ratio of Torsional Fatigue to Rotating Bending Fatigue in ... 291
structures of ferrite and pearlite areas are recognized in annealed rolled carbon steels (S20C,
S45C), and not in cast carbon steel (SC450) nor in S45C-H or S45C-DA material. Namely, the
former two are regarded as anisotropic materials, and the latter three are regarded as isotropic
materials (see Table 4).
In both tensile and torsional static tests, two types of specimens (S45C, SC450) were used.
The diameter of the specimen was 8 mm, and all specimens were electropolished to the depth
of about 20,um to remove the surface layer. For the observation of the specimen surface,
plastic replicas were taken from the surface after applying definite macroscopic strains. The
surface states were taken from the replicas to negative films with the optical microscope, then
digitized by using a film scanner and stored in the computer’s memory. The local strain was
measured using the image-processing method [21]. The macroscopic overall strains for the
tensile tests are Eg= 3, 6, 9, 12 %, and the macroscopic shear strains for the torsional test are
r, = 4.5, 9, 13.5, 18 %. The local strain for tensile test corresponds to the normal logarithmic
strain which is calculated from the elongation of an axial grid line, and the local strain for
torsional test corresponds to the shear strain which is calculated from the change of an
intersectional angle of two grid lines. The fine grid lines were also drawn on the surface of the
specimen with a diamond point needle [lo]. The width of the lines was made less than 111 m
and the depth of the lines less than 0.5 fi m. The mesh size of the grid is 20X 20 ,um.
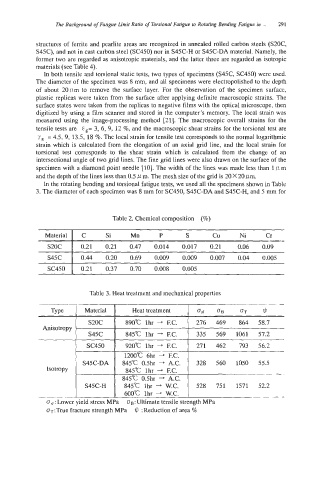
In the rotating bending and torsional fatigue tests, we used all the specimens shown in Table
3. The diameter of each specimen was 8 mm for SC450, S45C-DA and S45C-H, and 5 mm for
Table 2. Chemical composition (%)
SC450 I 0.21 0.37 0.70 0.008 0.005
Table 3. Heat treatment and mechanical properties
SC450 920°C lhr + F.C. 271 462 793 56.2
1200°C 6hr + F.C.
S45C-DA 845°C OShr + A.C. 328 560 1050 55.5
Isotropy 845°C lhr -+ F.C.
845°C 0.5hr + A.C.
S45C-H 845°C lhr + W.C. 528 751 1571 52.2
600°C lhr -+ W.C.