Page 312 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 312
296 7: FUKUDA AND H. NISITANI
From the above observation, it can be said that this type of crack initiation in the region near
the grain boundary is due to the nonconformity of deformation between pearlite and ferrite.
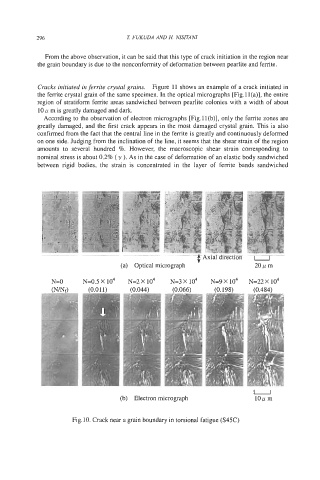
Cracks initiated in ferrite crystal grains. Figure 11 shows an example of a crack initiated in
the ferrite crystal grain of the same specimen. In the optical micrographs [Fig.ll(a)], the entire
region of stratiform ferrite areas sandwiched between pearlite colonies with a width of about
10 p m is greatly damaged and dark.
According to the observation of electron micrographs [Fig.ll(b)], only the ferrite zones are
greatly damaged, and the first crack appears in the most damaged crystal grain. This is also
confirmed from the fact that the central line in the ferrite is greatly and continuously deformed
on one side. Judging from the inclination of the line, it seems that the shear strain of the region
amounts to several hundred %. However, the macroscopic shear strain corresponding to
nominal stress is about 0.2% ( y ). As in the case of deformation of an elastic body sandwiched
between rigid bodies, the strain is concentrated in the layer of ferrite bands sandwiched
# Axial direction
(a) Optical micrograph 20p m
N=O N=0.5 X lo4 N=2 X lo4 N=3 X lo4 N=9 X lo4 N=22 X lo4
(Nrnf) (0.01 1) (0.044) (0.066) (0.198) (0.484)
I
b l
U
m
(b) Electron micrograph 10~
Fig. 10. Crack near a grain boundary in torsional fatigue (S45C)