Page 313 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 313
The Background of Fatigue Limit Ratio of Torsional Fatigue to Rotating Bending Fatigue in ... 297
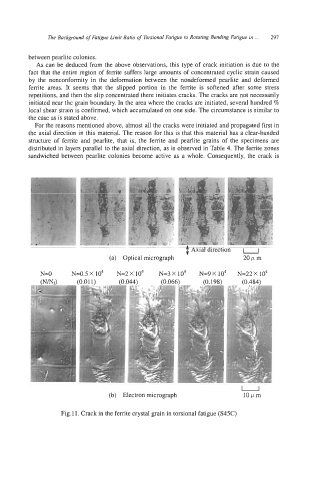
between pearlite colonies.
As can be deduced from the above observations, this type of crack initiation is due to the
fact that the entire region of ferrite suffers large amounts of concentrated cyclic strain caused
by the nonconformity in the deformation between the nondeformed pearlite and deformed
ferrite areas. It seems that the slipped portion in the ferrite is softened after some stress
repetitions, and then the slip concentrated there initiates cracks. The cracks are not necessarily
initiated near the grain boundary. In the area where the cracks are initiated, several hundred %
local shear strain is confirmed, which accumulated on one side. The circumstance is similar to
the case as is stated above.
For the reasons mentioned above, almost all the cracks were initiated and propagated first in
the axial direction in this material. The reason for this is that this material has a clear-banded
structure of ferrite and pearlite, that is, the ferrite and pearlite grains of the specimens are
distributed in layers parallel to the axial direction, as is observed in Table 4. The ferrite zones
sandwiched between pearlite colonies become active as a whole. Consequently, the crack is
I
(a) Optical micrograph 20~
m
N=O N=0.5 X IO4 N=2 X IO4 N=3 X IO4 N=9 X IO4 N=22 X lo4
) ( (0.48
3 ‘4J a’fw\ ”Vi 1.961 ‘9
U
(b) Electron micrograph 10pm
Fig.11. Crack in the ferrite crystal grain in torsional fatigue (S45C)